Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2022; 10(11): 3561-3572
Published online Apr 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i11.3561
Published online Apr 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i11.3561
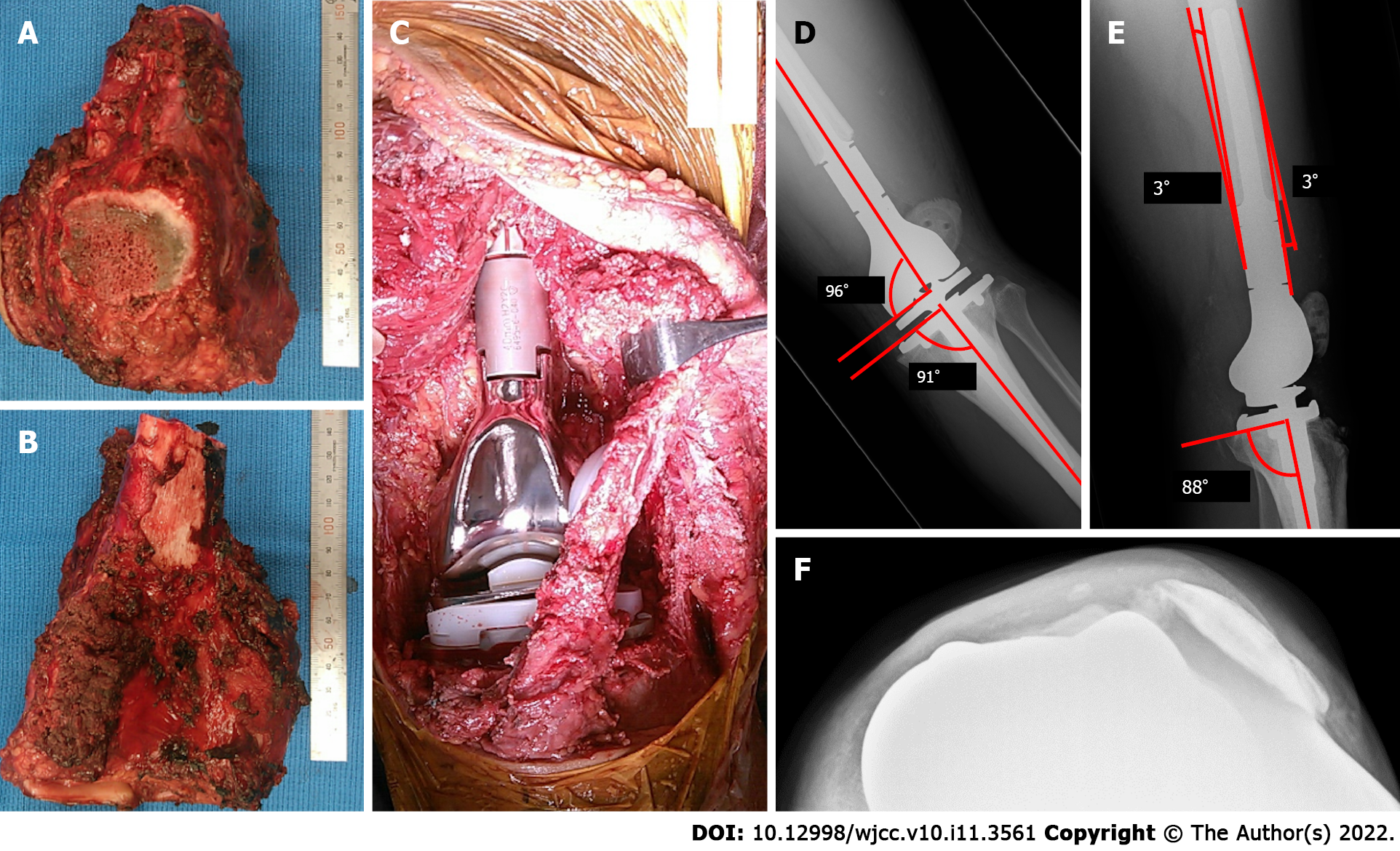
Figure 2 Photographic images during the primary surgery, and radiograph postoperatively.
A: The anterior view of the resected specimen and the longitudinally split patellar are shown; B: The posterior view of the resected specimen; C: After removal of the tumor, a tumor endoprosthesis was implanted; D and E: Patellar subluxation is found in radiograph at 1 wk postoperatively. The radiograph of the left knee shows the measurement of the coronal alignment of the femoral and tibial components. The overall anatomical alignment is defined as the angle between the femoral anatomical axis and the tibial anatomical axis (D); the lateral radiograph of the left knee shows the measurement of the sagittal alignment of the femoral and tibial components (E); F: The radiograph shows lateral luxation of the patellar at 1 mo postoperatively.
- Citation: Kubota Y, Tanaka K, Hirakawa M, Iwasaki T, Kawano M, Itonaga I, Tsumura H. Patellar dislocation following distal femoral replacement after extra-articular knee resection for bone sarcoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(11): 3561-3572
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i11/3561.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i11.3561