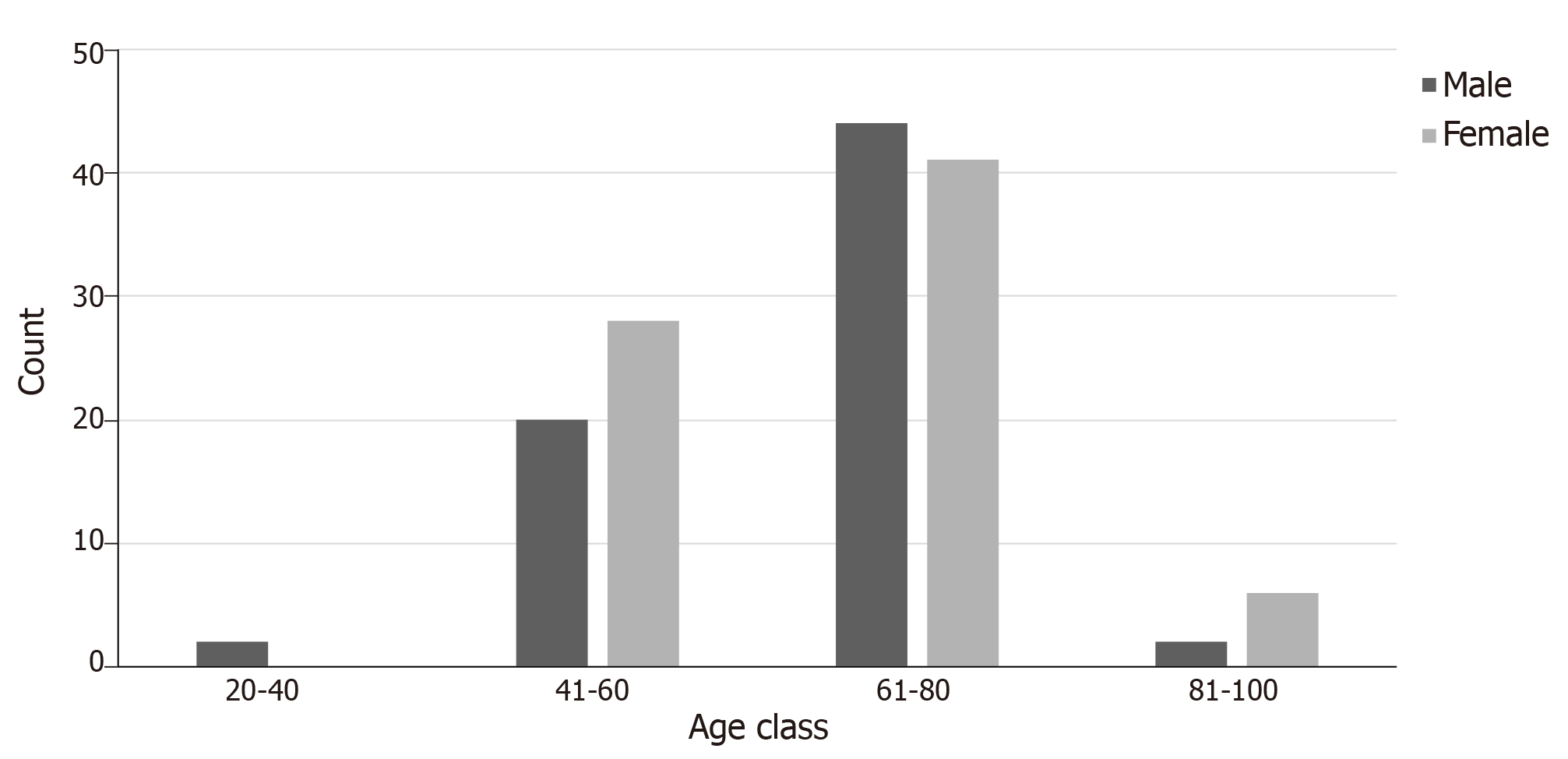Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2019; 7(21): 3474-3485
Published online Nov 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i21.3474
Published online Nov 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i21.3474
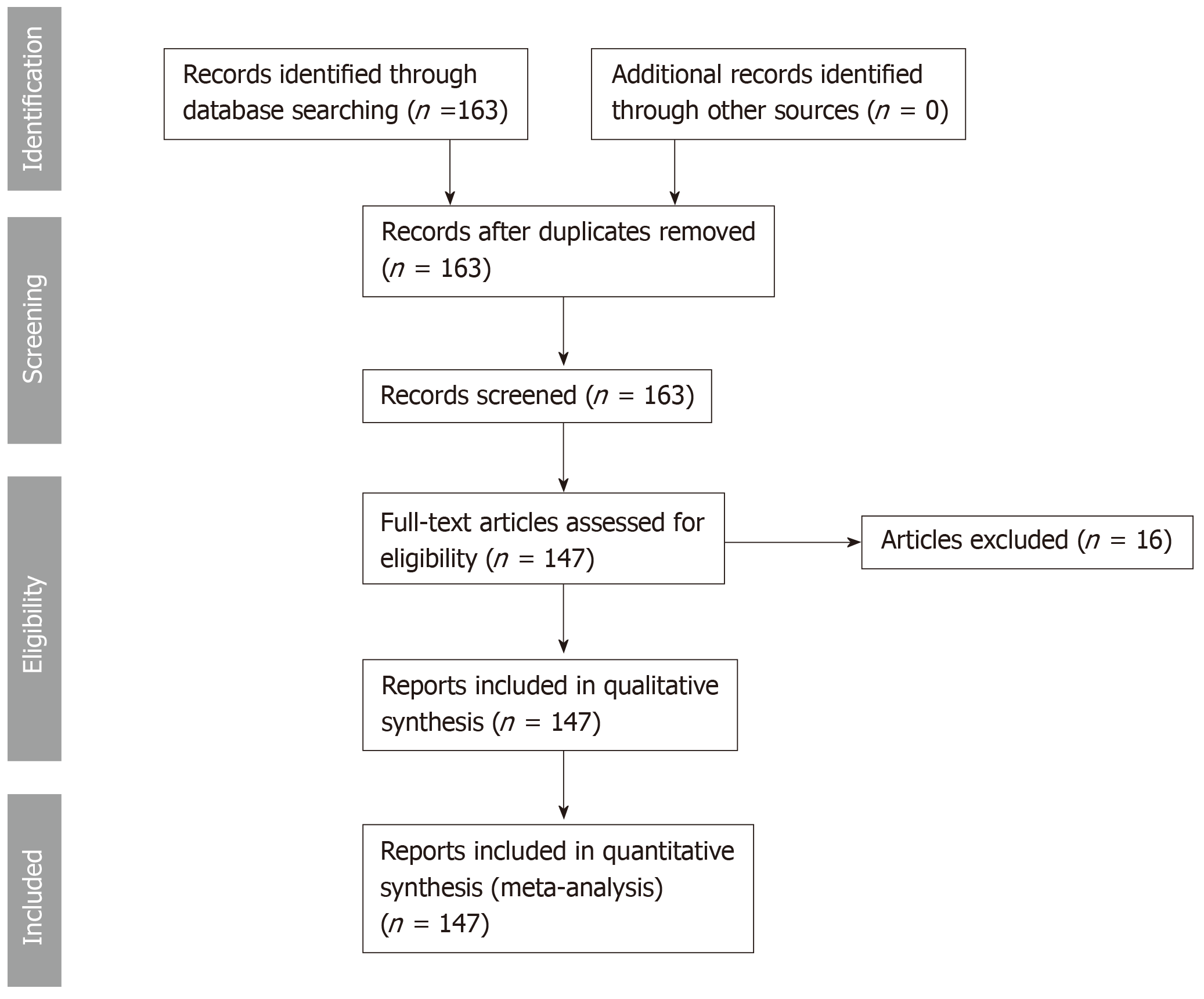
Figure 1 Systematic review design according to preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis criteria.
Figure 2 Age distribution among patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma and thyroid metastases.
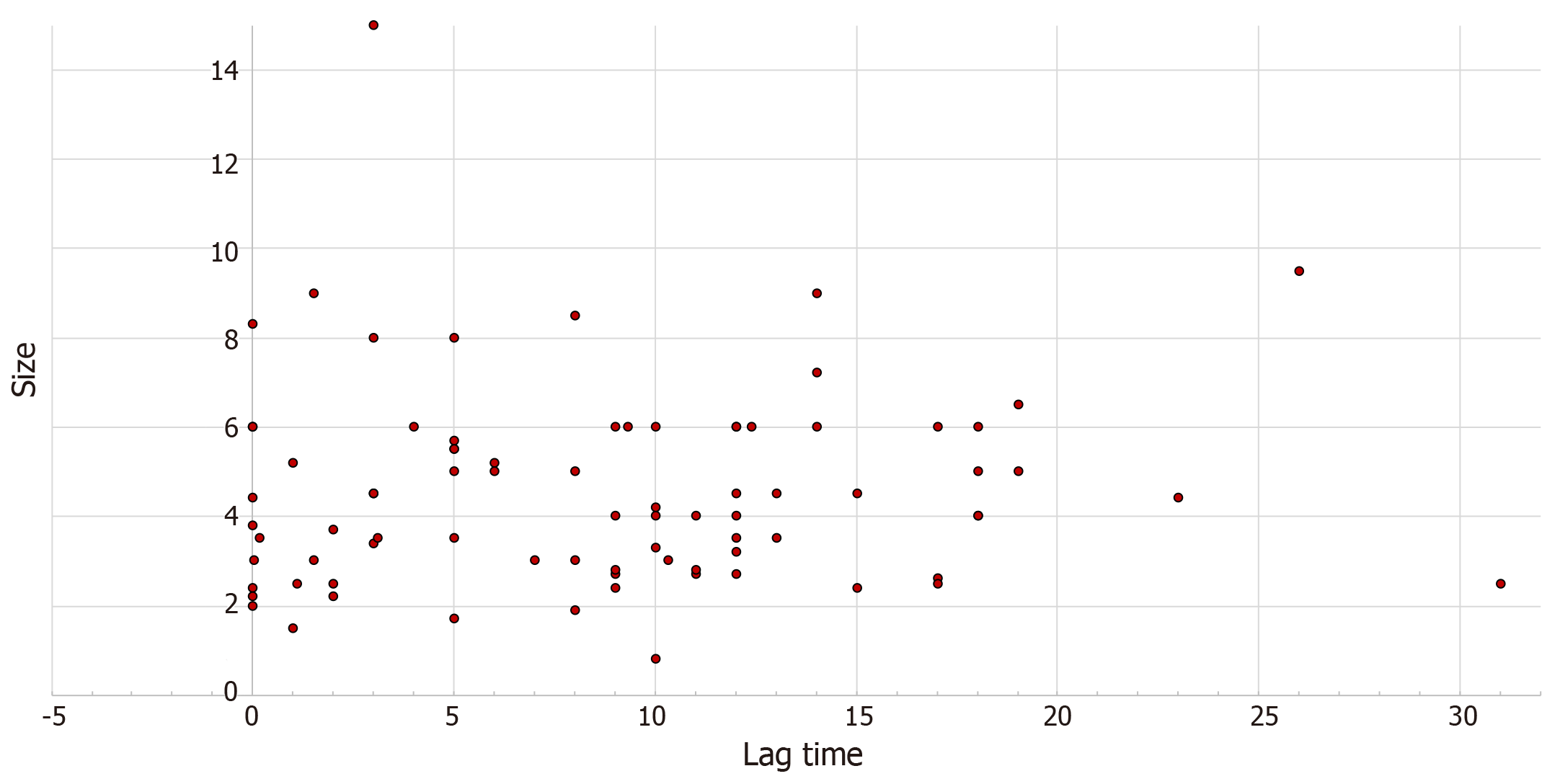
Figure 3 Association of thyroid metastatic lesion size with lag time from clear cell renal cell carcinoma diagnosis to diagnosis of thyroid metastasis (r = 0.
143, P = 0.1).
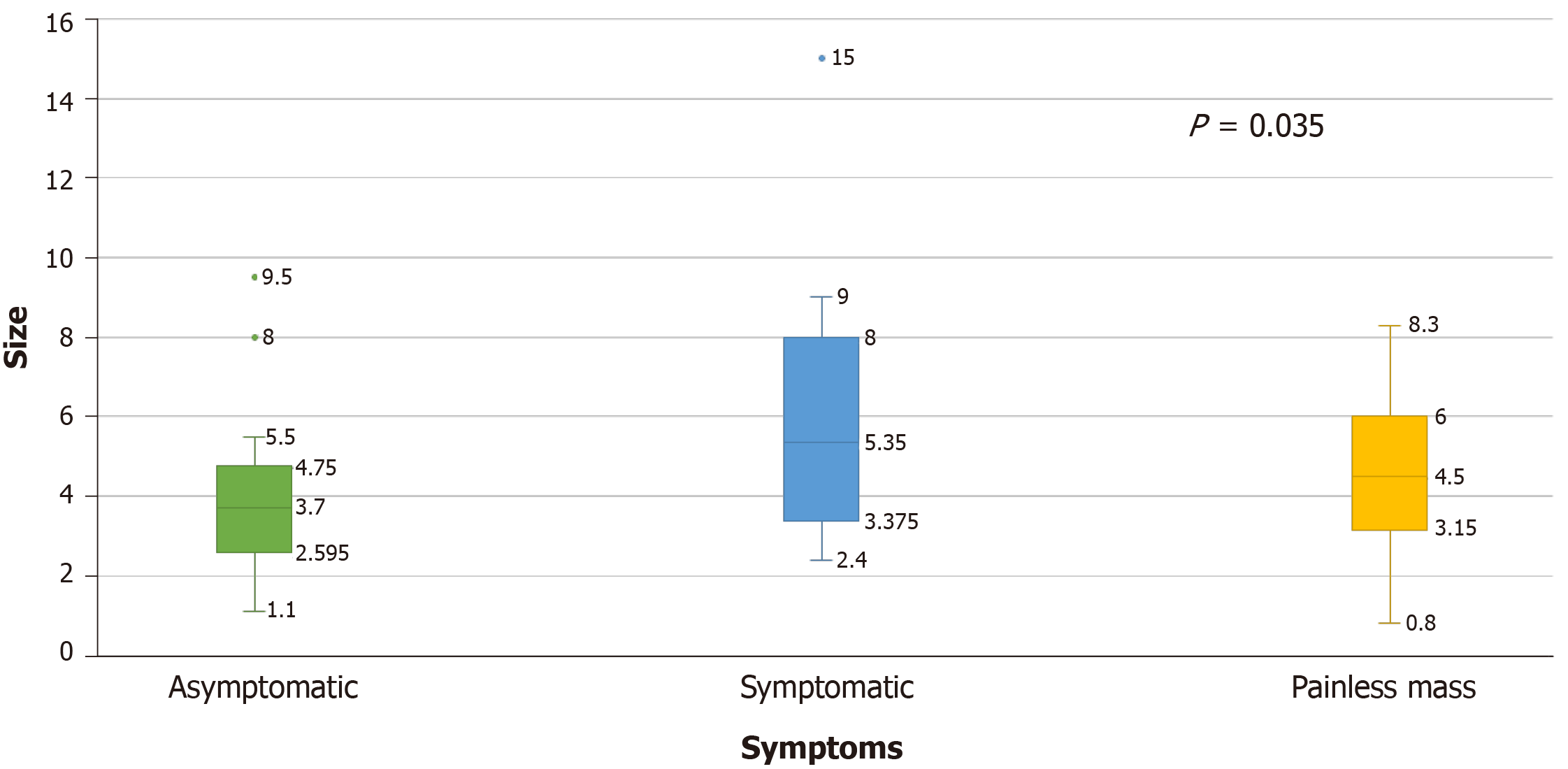
Figure 4 Mean tumor size in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients with thyroid metastases depending on their presenting symptoms.
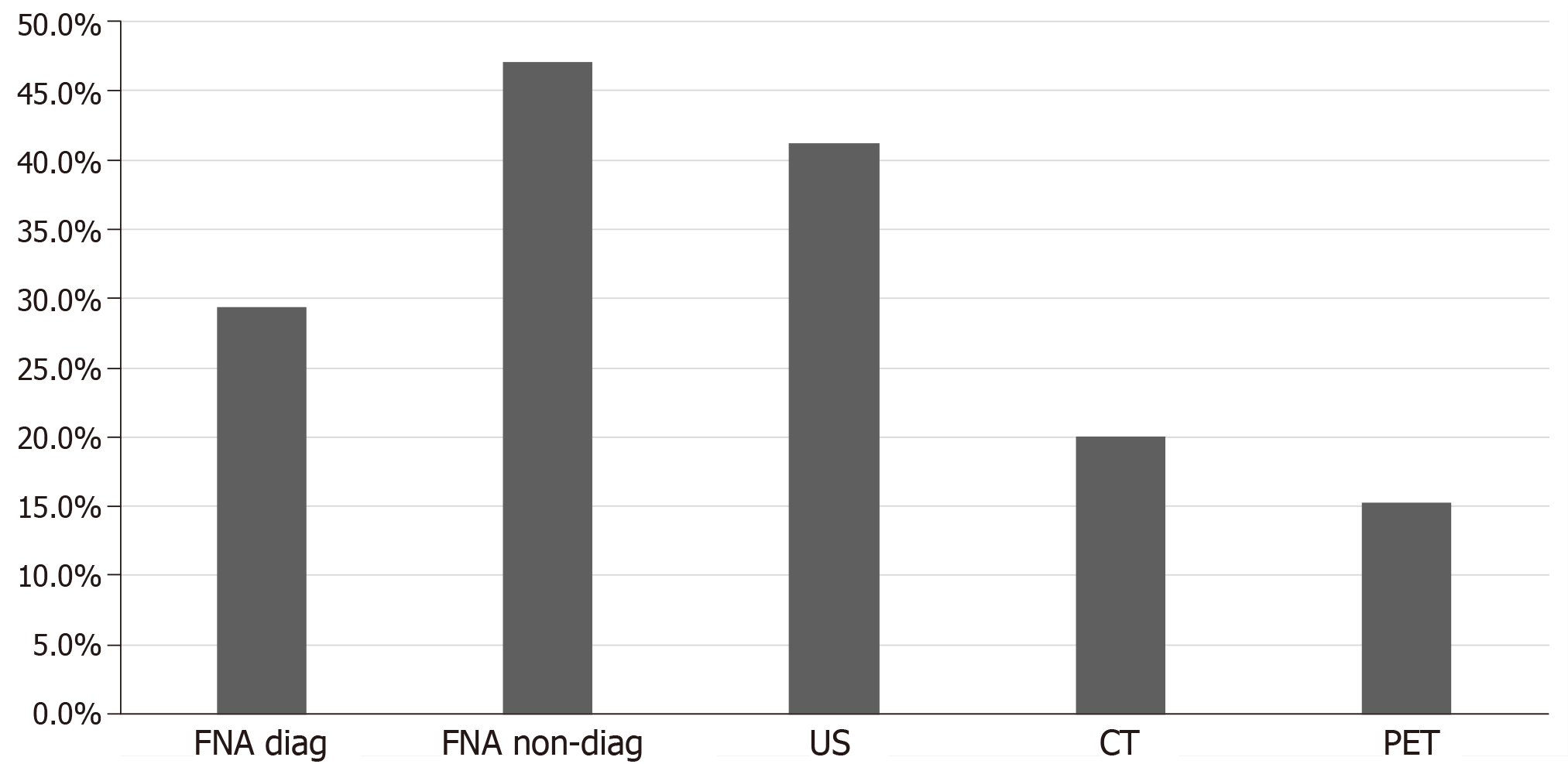
Figure 5 Diagnostic modality used for the diagnosis of thyroid metastasis in the studied population.
US: Ultrasound; CT: Computed tomography; PET: Positron emission tomography scan; FNA: Fine needle aspiration.
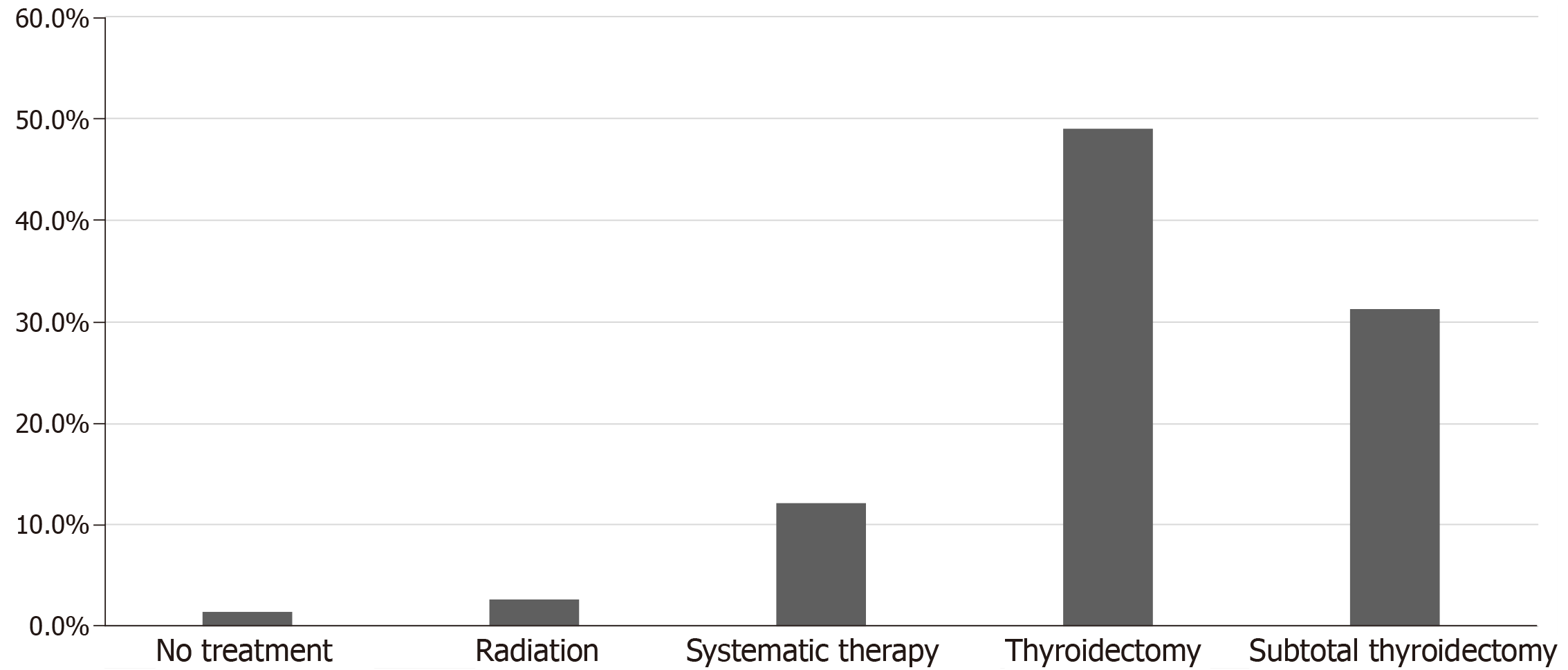
Figure 6 Treatment modalities used for thyroid metastases in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients in the studies population.
Systemic therapy included Interferon-a, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors, alkylating agent (capacitance), interlukin-2, unidentified chemotherapy.
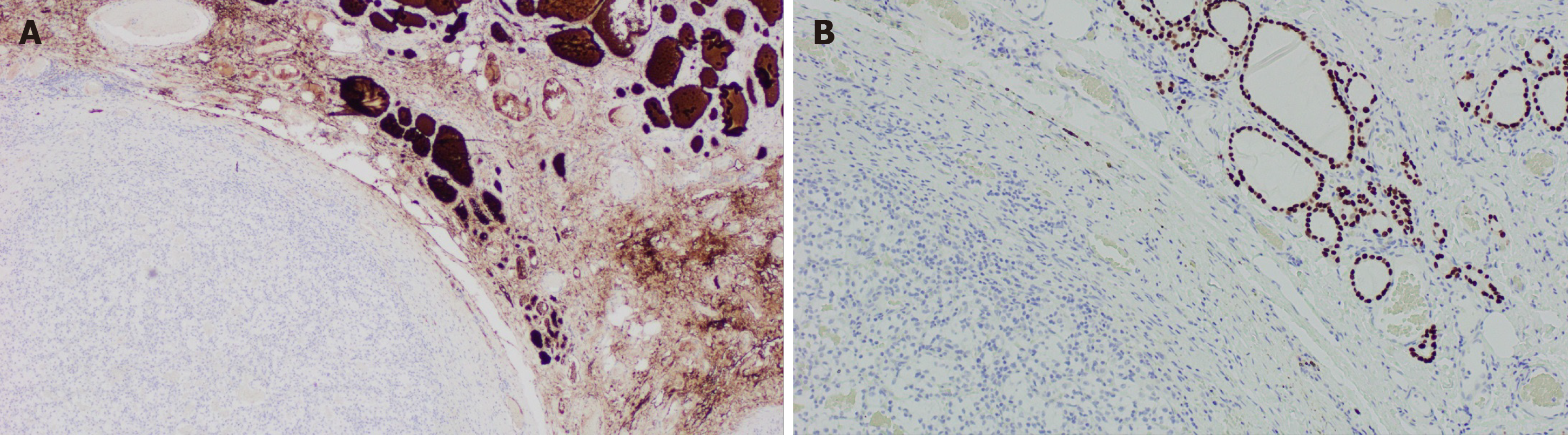
Figure 7 Illustrates immunohistochemical stains for thyroid transcription factor-1 and thyroglobulin in a case of clear cell renal cell carcinoma with thyroid metastases.
A: Immunohistochemically stain showing positive thyroglobulin on right side coinciding with normal thyroid architecture and negative on the left; B: Immunohistochemically stain for thyroid transcription factor-1 which is positive on the right correlating with normal thyroid architecture and negative on the left where the metastatic renal cell carcinoma is present (Magnification x 100).
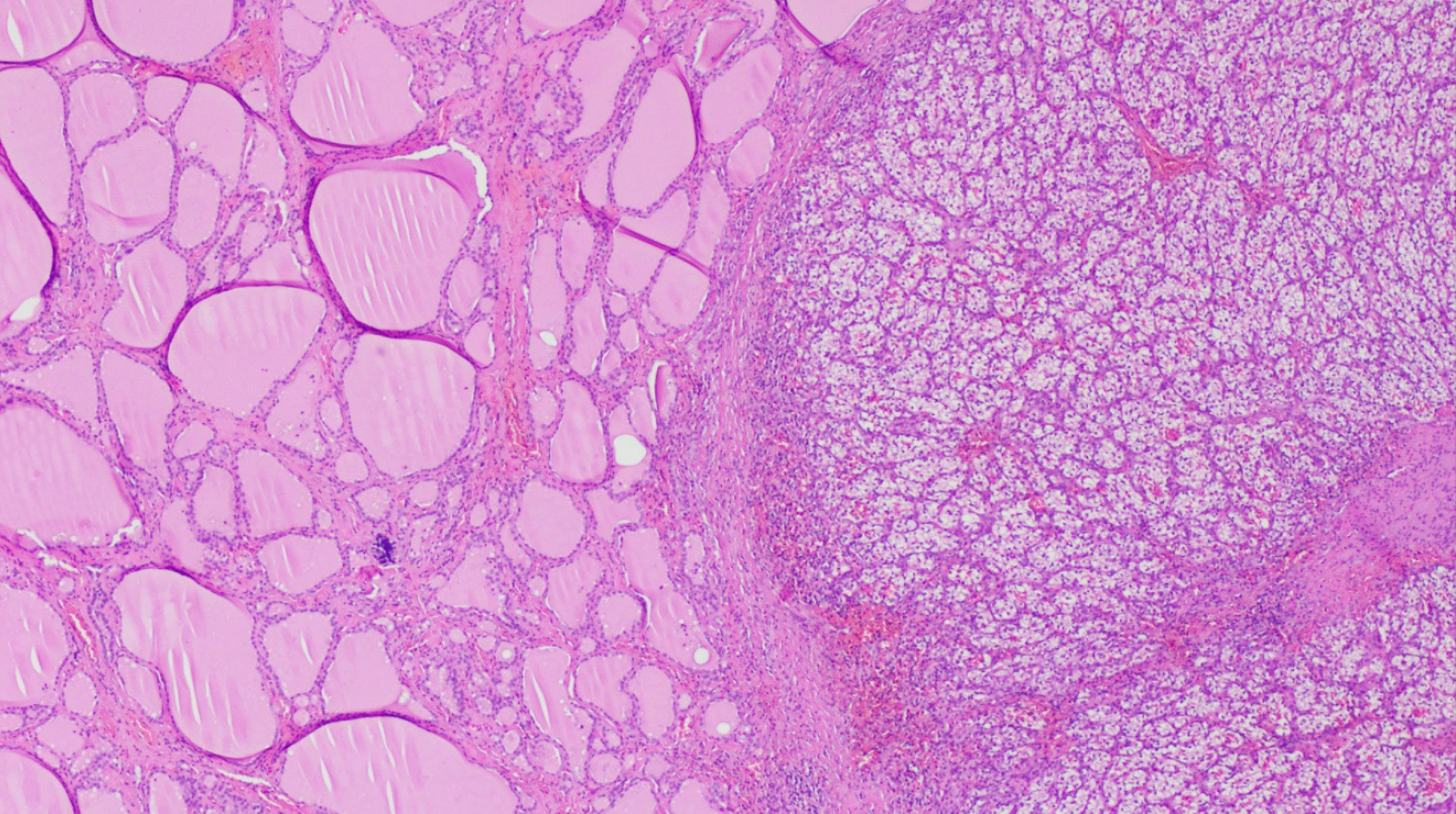
Figure 8 Hematoxylin-eosin staining showing benign thyroid tissue architecture (left) and metastatic renal cell carcinoma (right), (Magnification x 100).
- Citation: Khaddour K, Marernych N, Ward WL, Liu J, Pappa T. Characteristics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastases to the thyroid gland: A systematic review. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(21): 3474-3485
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i21/3474.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i21.3474