Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 21, 2022; 10(3): 1008-1015
Published online Jan 21, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.1008
Published online Jan 21, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.1008
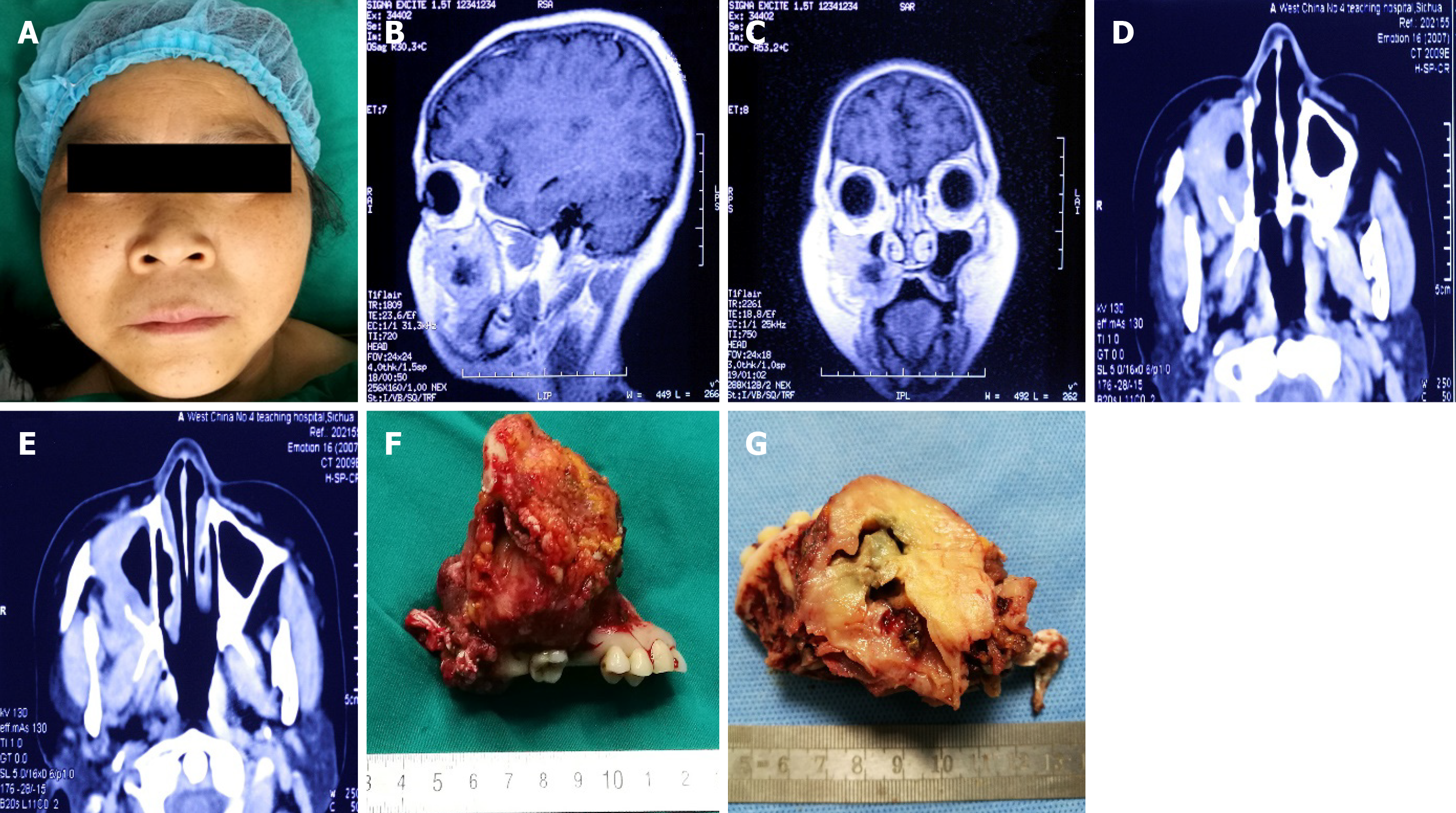
Figure 1 Characterization of imaging studies and gross finding.
A: Facial swelling measured about 4 cm in diameter on right side; B: Magnetic resonance imaging (sagittal section) demonstrated a soft tissue mass with a necrotic center compressing adjacent structures; C: Magnetic resonance imaging (coronal view) demonstrated a soft tissue mass with a necrotic center compressing the right maxilla; D and E: Computed tomography imaging demonstrated a soft tissue mass with a necrotic center compressing adjacent structures, red arrow showing the mass compressing the anterior wall of the right maxilla; F: The mass appeared to be lobulated and yellow-white measuring about 8 cm in diameter; G: On hemisection, the mass showed a well-circumscribed heterogenous lesion with a necrotic center.
Figure 2 Histological features of extracranial meningioma.
A and B: The specimen showed epithelioid lobulated tissue, separated by abundant collagen fibers (hematoxylin and eosin: × 100, × 40); C and D: The specimen showed abundant cytoplasm and indistinct cytoplasmic borders, arranged in whorled and lobulated patterns (hematoxylin and eosin: × 100, × 40).
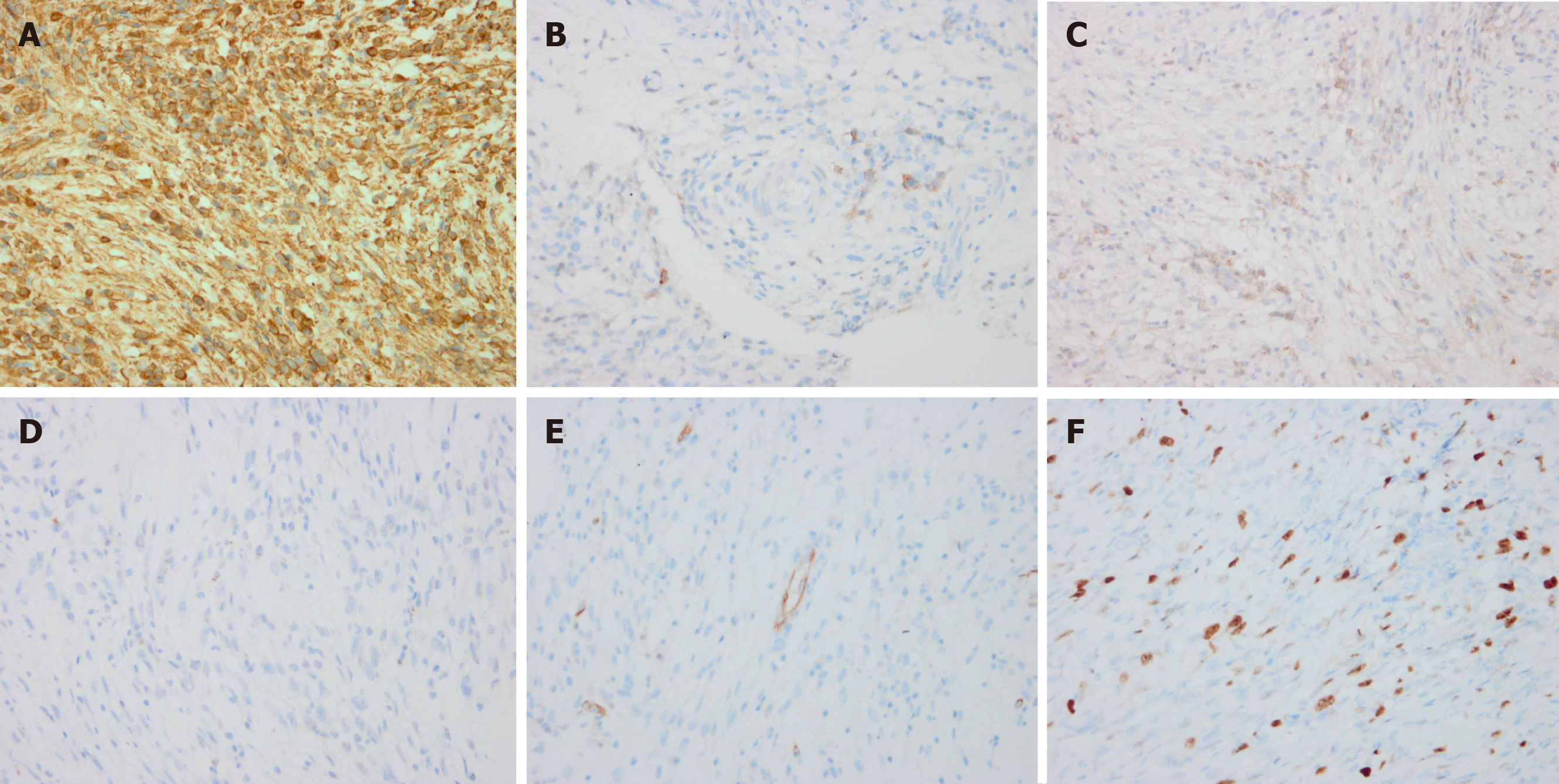
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical findings of the lesion.
A: The tumor cells were strongly positive for vimentin; B: The tumor cells were focally positive for epithelial membrane antigen; C: The tumor cells were focally positive for CD99; D: The tumor cells were negative for STAT6; E: The tumor cells were negative for CD34; F: The tumor cells were focally positive for Ki-67.
- Citation: Sigdel K, Ding ZF, Xie HX. Case of primary extracranial meningioma of the maxillary sinus presenting as buccal swelling associated with headache: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(3): 1008-1015
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i3/1008.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.1008