Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Methodol. Sep 26, 2017; 7(3): 101-107
Published online Sep 26, 2017. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i3.101
Published online Sep 26, 2017. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i3.101
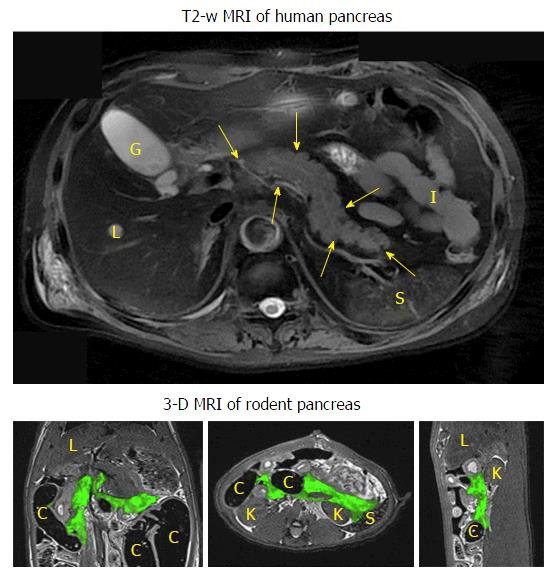
Figure 2 Typical human pancreatic magnetic resonance imaging vs rodent pancreatic magnetic resonance imaging.
The upper transverse image shows the human pancreas (contoured by arrowheads) as a solid organ adjacent to the liver (L), gallbladder (G), spleen (S), kidney (K) and small intestines (I). The lower 3-D images display the coronal (left), transverse (mid) and sagittal (right) views of the contrast-infused rat pancreas with green color coding, adjacent to the liver (L), spleen (S), kidney (K) and colon (C). MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Citation: Yin T, Liu Y, Peeters R, Feng Y, Ni Y. Pancreatic imaging: Current status of clinical practices and small animal studies. World J Methodol 2017; 7(3): 101-107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v7/i3/101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v7.i3.101