Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Methodol. Mar 26, 2016; 6(1): 112-117
Published online Mar 26, 2016. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v6.i1.112
Published online Mar 26, 2016. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v6.i1.112
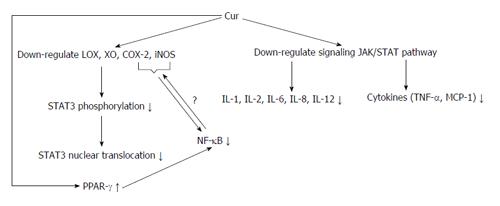
Figure 3 Mechanisms of anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin in vivo.
Curcumin (Cur) down-regulates some of the factors involved in inflammation, inhibiting NF-κB activation and causing its anti-inflammatory effects. Also, Cur with increasing PPAR-γ expression directly inhibits NF-κB activation. NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; TNF: Tumor necrosis factors; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; IL: Interleukins; LOX: Lipoxygenase; COX: Cyclooxygenase; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; PPAR-γ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; XO: Xanthine oxidase.
- Citation: Mazidi M, Karimi E, Meydani M, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Ferns GA. Potential effects of curcumin on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ in vitro and in vivo. World J Methodol 2016; 6(1): 112-117
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v6/i1/112.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v6.i1.112