Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Methodol. Sep 26, 2015; 5(3): 127-135
Published online Sep 26, 2015. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v5.i3.127
Published online Sep 26, 2015. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v5.i3.127
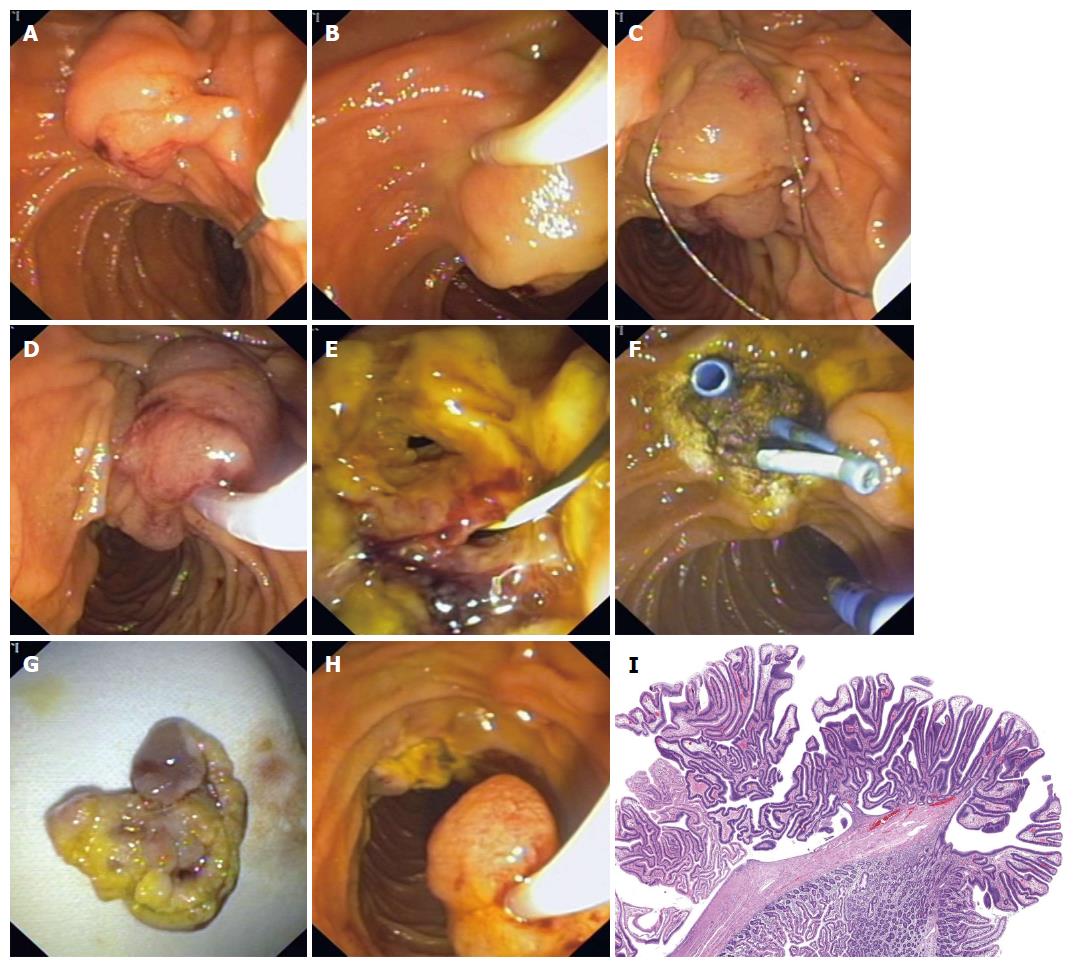
Figure 1 Technique of en-bloc ampullectomy.
A: Lesion is identified; B: Submucosal (saline + epinephrine) injection; C: With the snare tip anchored above the papillary mound the entire papilla is snared; D: Check mobility and ensure the snare is firmly closed; E: En-bloc ampullary resection. Biliary and pancreatic (guidewire) orifice is identified; F: Biliary and pancreatic stents are placed. Adjuvant APC therapy is applied; G: Tissue retrieval with the snare; H: Ampullectomy specimen; I: Ampullary adenoma: tubulovillous architecture that shows neoplastic epithelial cells with pseudostratified and enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei. Adjacent there is normal duodenal mucosa. (HE: 20 ×). (Courtesy of Mercedes Hernando, MD). APC: Argon plasma coagulation.
- Citation: Espinel J, Pinedo E, Ojeda V, Rio MGD. Endoscopic management of adenomatous ampullary lesions. World J Methodol 2015; 5(3): 127-135
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v5/i3/127.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v5.i3.127