Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Methodol. Dec 26, 2014; 4(4): 197-218
Published online Dec 26, 2014. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v4.i4.197
Published online Dec 26, 2014. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v4.i4.197
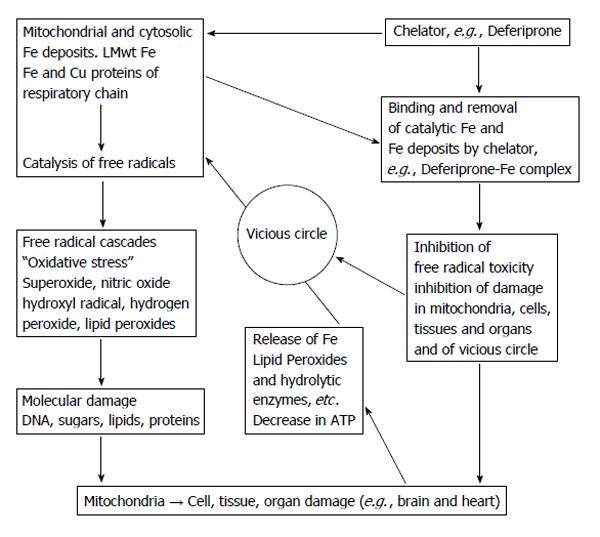
Figure 2 The mode of chelating and antioxidant activity of deferiprone in Friedreich Ataxia.
Deferiprone can chelate intracellular and intramitochondrial iron deposits and labile low molecular weight (LMwt) iron, which are responsible for the catalytic formation of toxic free radicals and toxic byproducts. It can inhibit iron toxicity related damage to the heart and brain of Friedreich ataxia patients.
- Citation: Kolnagou A, Kontoghiorghe CN, Kontoghiorghes GJ. Transition of Thalassaemia and Friedreich ataxia from fatal to chronic diseases. World J Methodol 2014; 4(4): 197-218
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v4/i4/197.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v4.i4.197