Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Methodol. Mar 26, 2013; 3(1): 11-18
Published online Mar 26, 2013. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v3.i1.11
Published online Mar 26, 2013. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v3.i1.11
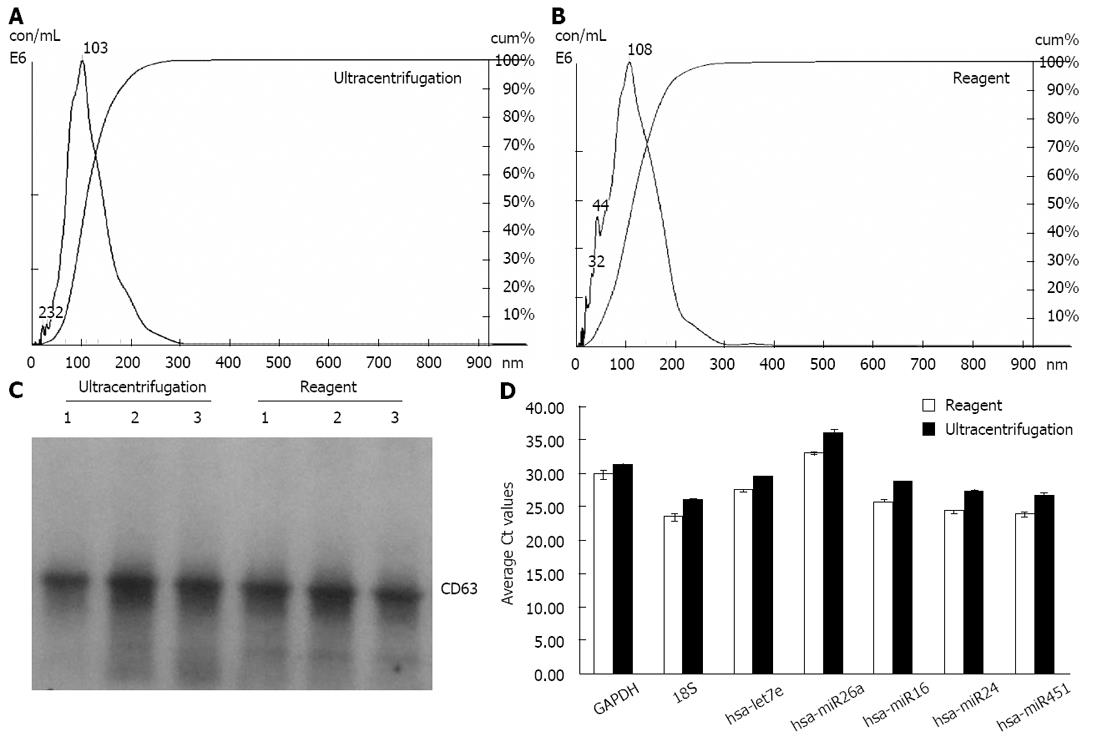
Figure 1 Exosomes isolated from cell media using the reagent are comparable to ultracentrifugation preparations.
A, B: Analysis of exosomes recovered from HeLa cell culture media using the Total exosome isolation reagent (from cell culture media) and ultracentrifugation protocol-by Nanosight® LM10 instrument. The profiles are essentially very-finely segmented histograms, indicating the number of particles per mL (in millions) for each size in bins of 1 nm increment from 0 to 1000 nm; C: Western blot analysis for the presence of exosomal marker protein CD63 in cell culture media derived samples. Exosomes from three separate HeLa cell culture media preparations (isolated with either the Total exosome isolation reagent (from cell culture media) or ultracentrifugation) were separated on a Novex 4%-20% Tris-Glycine Gel under denaturing, non-reducing conditions. Standard Western blot procedures with anti-CD63 antibodies were used to detect cell media derived exosomal protein markers; D: Analysis of the exosomal miRNA and mRNA levels in HeLa cell culture media derived samples by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). RNA was isolated using the Total exosome RNA and protein isolation kit from exosomes extracted using the Total exosome isolation reagent (from cell culture media) and the ultracentrifugation protocol. Levels of five microRNAs (let7e, miR26a, miR16, miR24 and miR451) and two mRNAs [glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and 18S] were quantified by qRT-PCR using TaqMan assays and reagents.
- Citation: Zeringer E, Li M, Barta T, Schageman J, Pedersen KW, Neurauter A, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, Vlassov AV. Methods for the extraction and RNA profiling of exosomes. World J Methodol 2013; 3(1): 11-18
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v3/i1/11.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v3.i1.11