Copyright
©2012 Baishideng.
World J Methodol. Oct 26, 2012; 2(5): 33-41
Published online Oct 26, 2012. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v2.i5.33
Published online Oct 26, 2012. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v2.i5.33
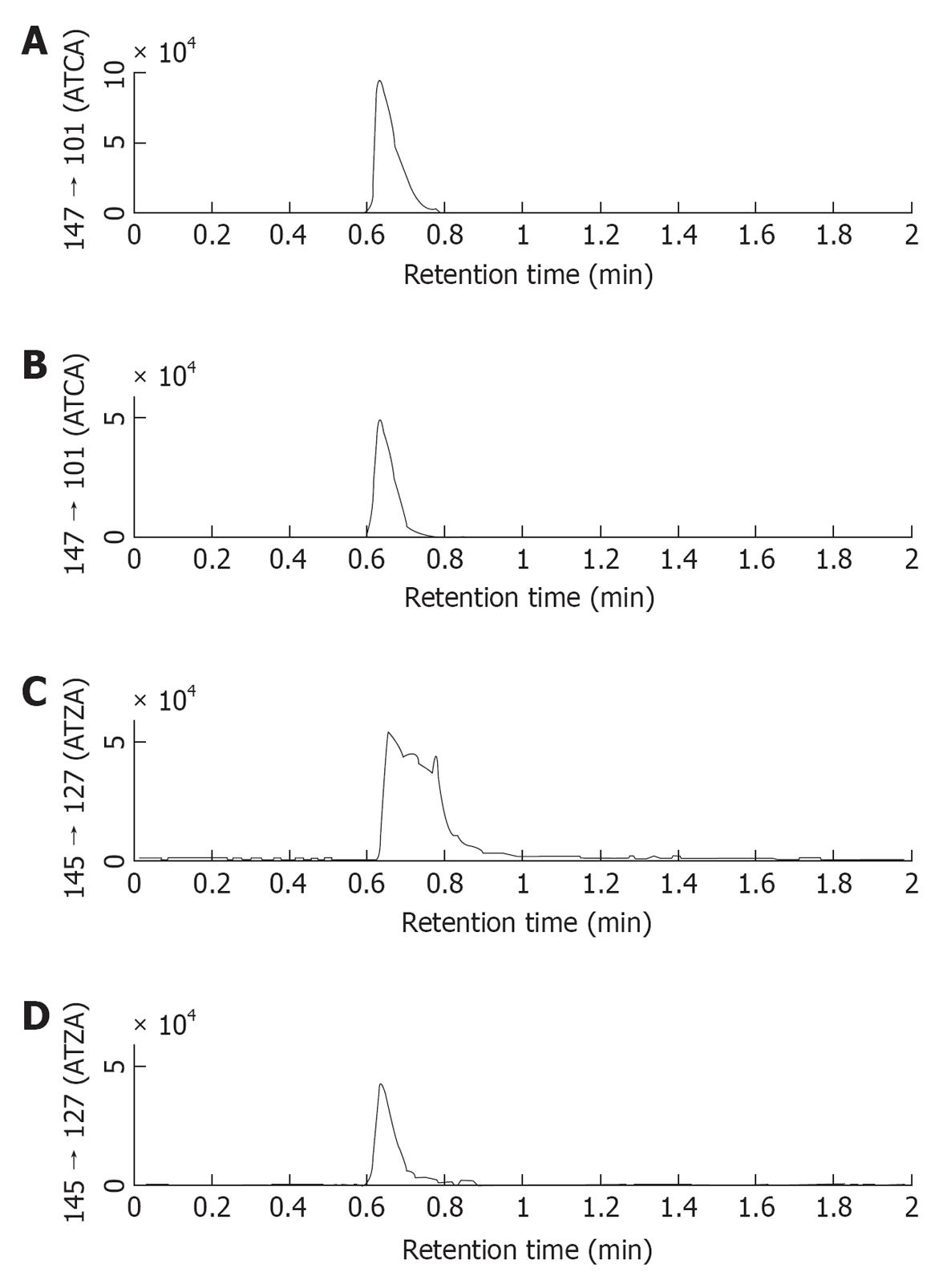
Figure 6 2-aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid concentration in mice plasma after different doses of potassium cyanide (endogenous level = 0 mg/kg body weight dose of potassium cyanide).
Mice received three different sublethal doses (6, 8 and 10 mg/kg) of cyanide subcutaneously (3 mice/doses) and were terminated 15 min after cyanide exposure. A significant correlation of cyanide dose vs 2-aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid (ATCA) concentration in plasma samples was observed. ATCA concentration in mice plasma samples was increased from 189 ± 28 ng/mL (n = 3 mice) for endogenous level [0 mg/kg body weight dose of potassium cyanide (KCN)] to 413 ± 66 ng/mL (n = 3 mice) for 10 mg/kg body weight dose of KCN.
- Citation: Yu JC, Martin S, Nasr J, Stafford K, Thompson D, Petrikovics I. LC-MS/MS analysis of 2-aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid as a forensic biomarker for cyanide poisoning. World J Methodol 2012; 2(5): 33-41
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v2/i5/33.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v2.i5.33