Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
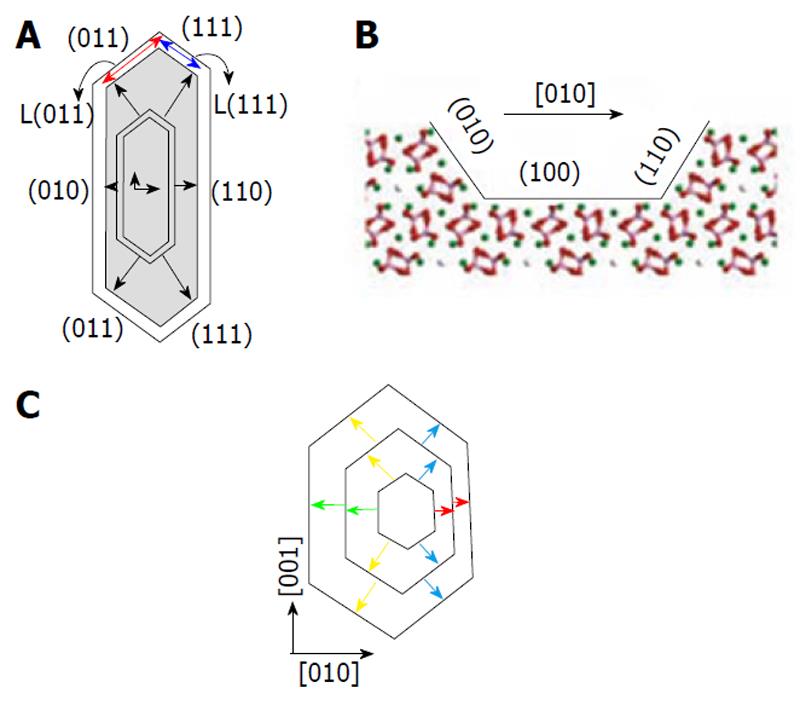
Figure 3 A typical etch pit on the surface of calcium apatites.
A: Top view and a model of its evolution during dissolution. Arrows represent relative step velocities displaying different facets; B: View through the [001] direction in the (100) surface. The exposed step faces can be seen to be un-equivalent owing to the opposite orientations of the orthophosphate groups. Reprinted from Ref. [118] with permission; C: Schematic of the evolution of hexagonal etch pits. Four differently colored arrows represent relative step velocities. Reprinted from Ref. [120] with permission.
- Citation: Dorozhkin SV. Dissolution mechanism of calcium apatites in acids: A review of literature. World J Methodol 2012; 2(1): 1-17
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v2/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v2.i1.1