Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Methodol. Dec 20, 2024; 14(4): 93461
Published online Dec 20, 2024. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i4.93461
Published online Dec 20, 2024. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i4.93461
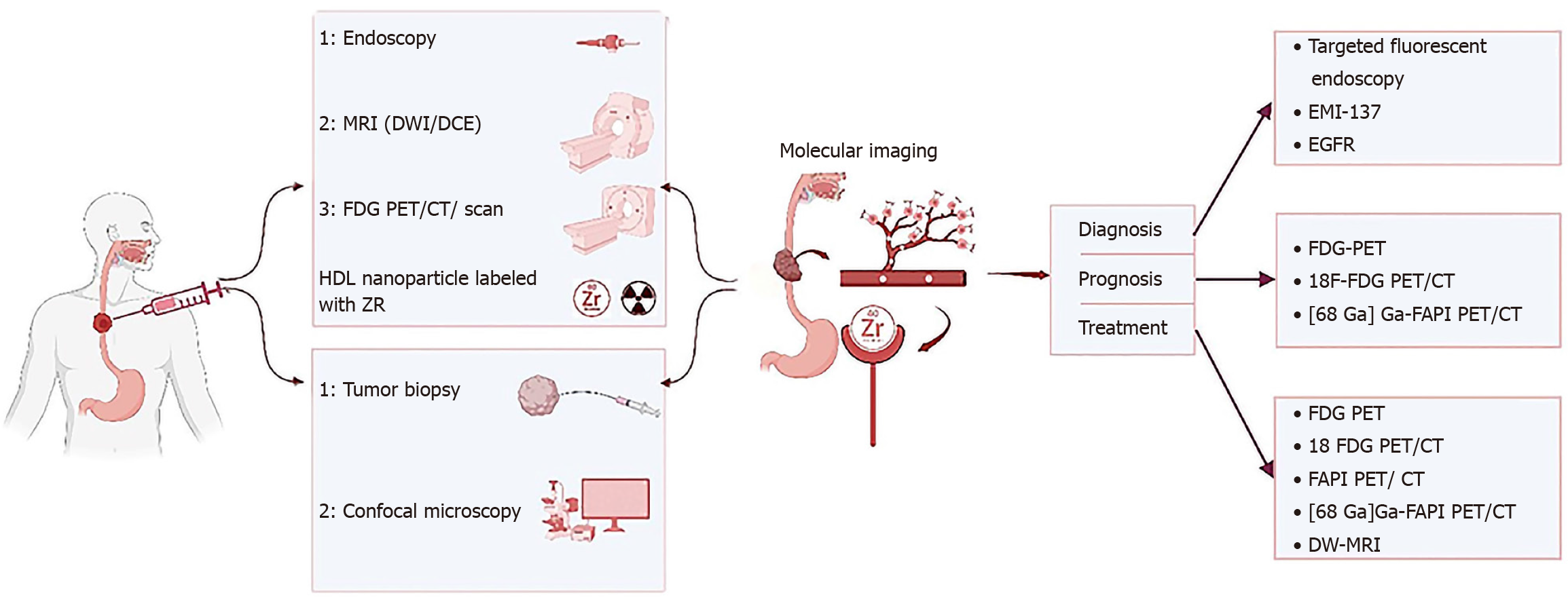
Figure 3 Role of personalized medicine and molecular imaging in esophagus cancers.
The function of molecular imaging and personalized medicine in esophageal cancers such as squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma including simultaneous or even initial and final examinations in the way of collecting temporal and personal information (specific to each person) in the diagnosis process including the collection of human samples, biopsy and blood samples and so on, all kinds of imaging modalities like endoscopy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [diffusion-weighted (DWI)/dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging], [positron emission tomography (PET), PET computed tomograph (CT) and bound with F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)] and also in the path of determining disease prognosis with PET types including FDG-PET, [68 Ga] Ga-FAPI PET/CT, and 18F-FDG PET/CT. Treatment with dedicated modalities FDG-PET, [68 Ga] Ga-FAPI PET/CT, 18F-FDG PET/CT, and DWI-MRI and it is tried in each stage of the currency, from the beginning of data collection to diagnosis, determining prognosis, treatment, response to treatment, assessment of relapse and follow-up, is the most appropriate and accurate and personalized solution possible based on personalized medicine in determining the dose of the substances used in the modalities imaging, choosing the most suitable imaging modality and binding element, the amount of medical treatment (drugs, amount and type of drug), and even all kinds of combined solutions with surgery and radiation therapy should be used. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; DW: Diffusion-weighted; PET: Positron emission tomography; CT: Computed tomography; FDG: F-fluorodeoxyglucose; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor.
- Citation: Fathi M, Taher HJ, Al-Rubiae SJ, Yaghoobpoor S, Bahrami A, Eshraghi R, Sadri H, Asadi Anar M, Gholamrezanezhad A. Role of molecular imaging in prognosis, diagnosis, and treatment of gastrointestinal cancers: An update on new therapeutic methods. World J Methodol 2024; 14(4): 93461
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v14/i4/93461.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v14.i4.93461