Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Methodol. Mar 20, 2024; 14(1): 89723
Published online Mar 20, 2024. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i1.89723
Published online Mar 20, 2024. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i1.89723
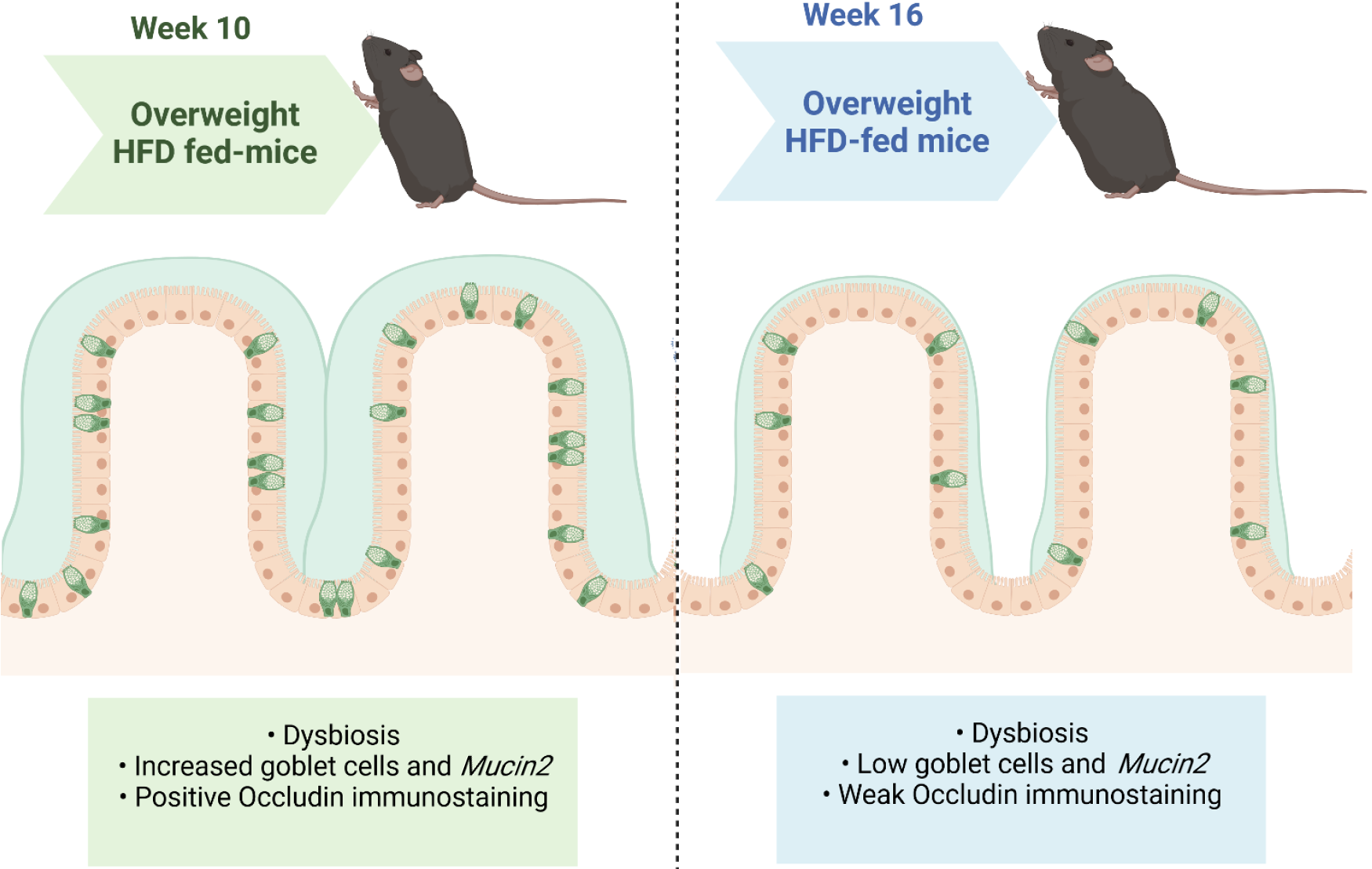
Figure 4 Summary of the main results.
The animals fed the high-fat diet for 10 wk (HF10) had overweight, increased goblet cell numerical density, and Mucin2 expression as a compensatory mechanism to prevent injury from the HFD. However, after 16 wk, HFD-fed mice remained overweight and had a greater body mass than the HF10 group but had a decreased goblet cell number and Mucin2 expression. Therefore, HF16 mice exhibited a completely disarranged intestinal ultrastructure, with damaged tight junctions and negative occludin immunostaining. Created with Biorender (www.biorender.com). HFD: High-fat diet.
- Citation: Miranda CS, Santana-Oliveira DA, Vasques-Monteiro IL, Dantas-Miranda NS, Glauser JSO, Silva-Veiga FM, Souza-Mello V. Time-dependent impact of a high-fat diet on the intestinal barrier of male mice. World J Methodol 2024; 14(1): 89723
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v14/i1/89723.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v14.i1.89723