Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Methodol. Mar 20, 2022; 12(2): 64-82
Published online Mar 20, 2022. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i2.64
Published online Mar 20, 2022. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i2.64
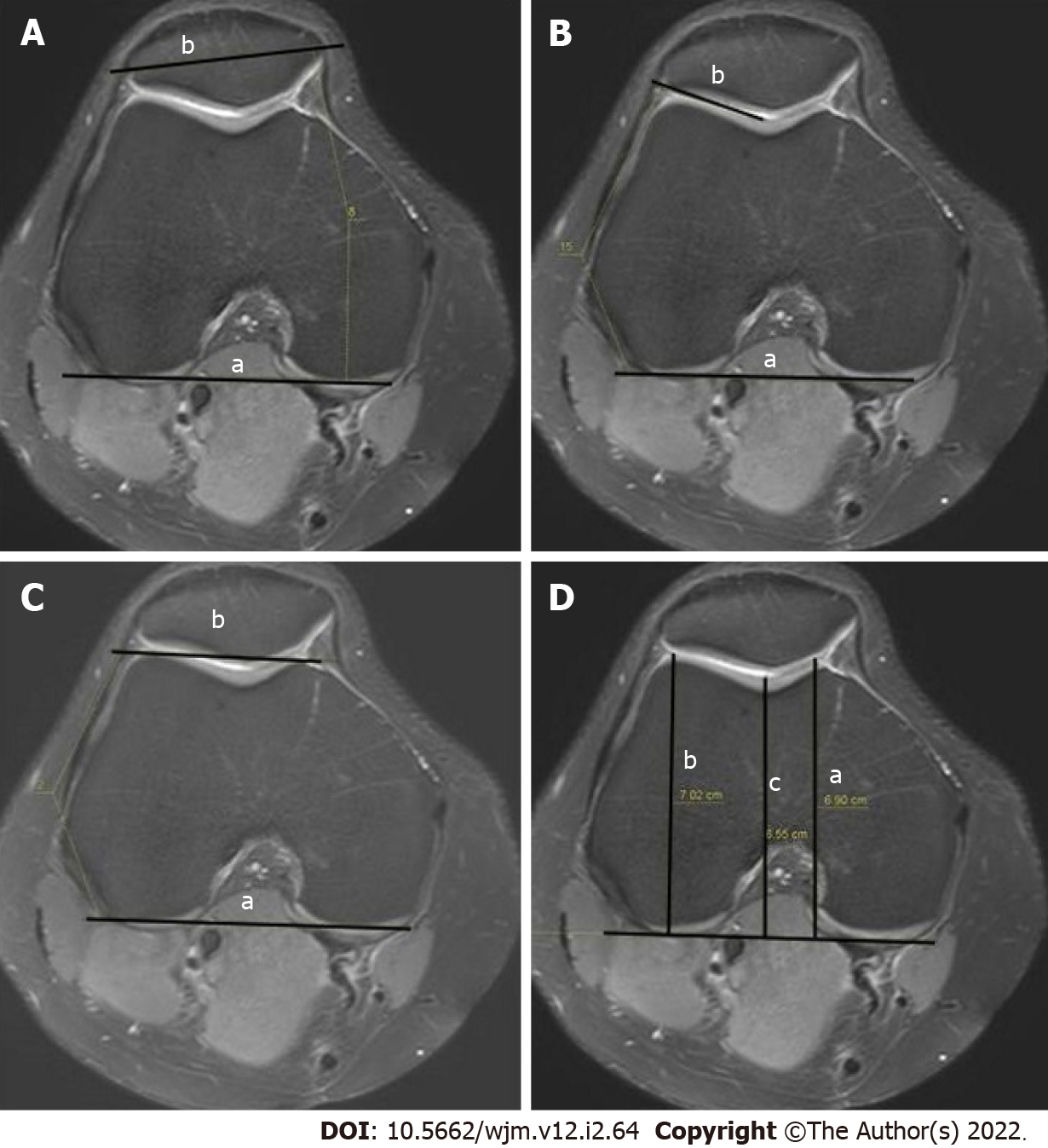
Figure 6 Measurement.
A: Patellar tilt (a: The line joining the posterior femoral condyles; b: The transverse patellar axis); B: Lateral trochlear inclination (a: The line tangent to the posterior edge of the femoral condyles; b: The line drawn tangent to the lateral facet); C: Trochlear angle (a: the angle between the line passing posteriorly to both femoral condyles; b: The line joining the foremost parts of the medial and lateral facets); D: Trochlear depth in axial magnetic resonance imaging (a: The maximal anterior-posterior diameter of the medial femoral condyle; b: The maximal anterior-posterior diameter of the lateral condyle; c: The minimum distance of the deepest point of the trochlea).
- Citation: Ormeci T, Turkten I, Sakul BU. Radiological evaluation of patellofemoral instability and possible causes of assessment errors. World J Methodol 2022; 12(2): 64-82
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v12/i2/64.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v12.i2.64