Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Methodol. May 20, 2021; 11(3): 23-45
Published online May 20, 2021. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v11.i3.23
Published online May 20, 2021. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v11.i3.23
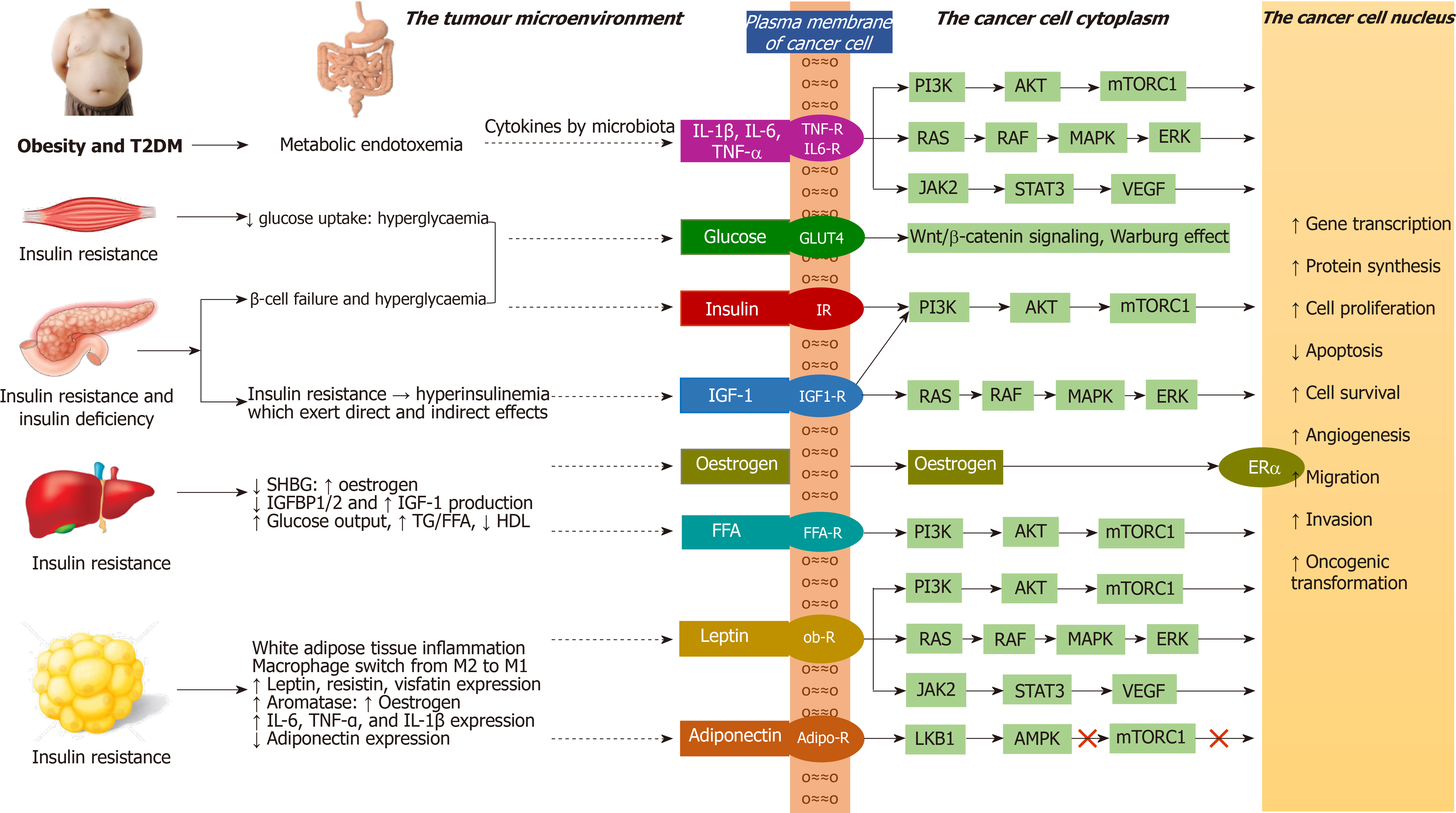
Figure 1 The overall pathophysiological mechanisms linking obesity and diabetes to cancer with associated intracellular signalling.
IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor-α; IR: Insulin receptor; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1; IGF-1R: Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; IGFBP: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein; FFA: Free fatty acid; FFF-R: Free fatty acid receptor; ER-α: Oestrogen receptor-α; Ob-R: Leptin-receptor; Adipo-R: Adiponectin-receptor; SHBG: Sex hormone binding globulin; TG: Triglyceride; HDL: High density lipoprotein; PI3K: Phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; mTORC1: Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1); RAS: Rat sarcoma; RAF: Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular-regulated kinase; JAK2: Janus kinase-2; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; HIF-1α: Hypoxia inducible factor-1α; LKB1: Liver kinase B1; AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Citation: Fernandez CJ, George AS, Subrahmanyan NA, Pappachan JM. Epidemiological link between obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus and cancer. World J Methodol 2021; 11(3): 23-45
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v11/i3/23.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v11.i3.23