Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Transl Med. Dec 12, 2015; 4(3): 113-122
Published online Dec 12, 2015. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.113
Published online Dec 12, 2015. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.113
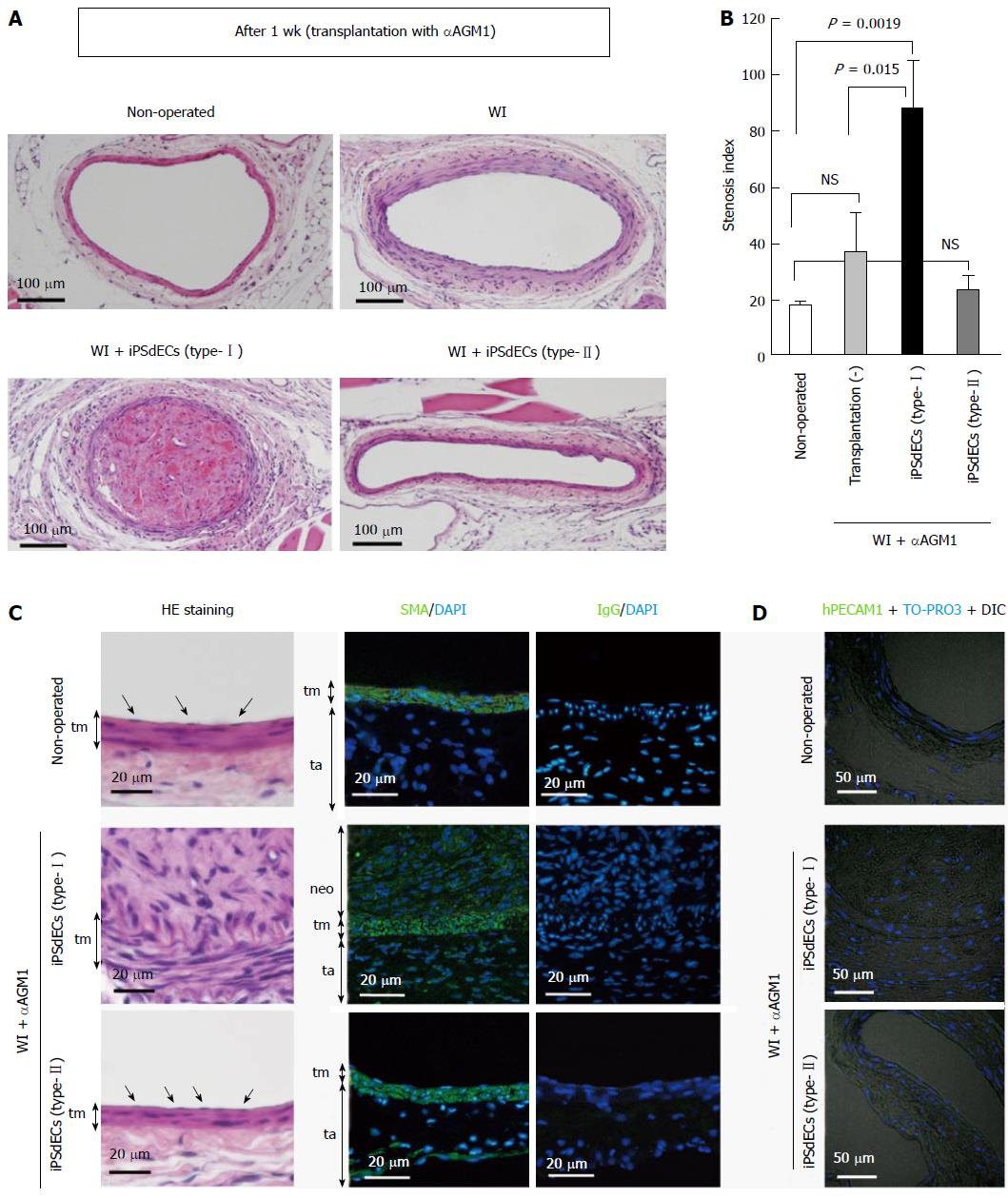
Figure 3 Histological analyses after three weeks.
Histologies of WI-operated femoral arteries after three weeks from PVVT in mice regularly administrated with aAGM1 were examined. A: Photographs of HE-stained samples at low magnification; B: Stenosis indexes were calculated and statistically analyzed by student-t test. Data were presented as average (Av) ± standard deviation (SD). Experiments were performed using three mice for each condition (n = 3); C and D: High magnification photographs of the samples with HE staining (C, left), immunostaining using anti-smooth muscle actin (SMA) antibody with nuclear counterstaining by DAPI (C, right) and immunostaining using anti-hPECAM1antibody with DIC and nuclear counterstaining by DAPI (D). WI: Wire injury; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell; iPSdECs: iPSC-derived VECs; αAGM1: Anti-asialo GM1 monoclonal antibody.
- Citation: Nishio M, Nakahara M, Saeki K, Fujiu K, Iwata H, Manabe I, Yuo A, Saeki K. Pro- vs anti-stenotic capacities of type-I vs type-II human induced pluripotent-derived endothelial cells. World J Transl Med 2015; 4(3): 113-122
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6132/full/v4/i3/113.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.113