Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
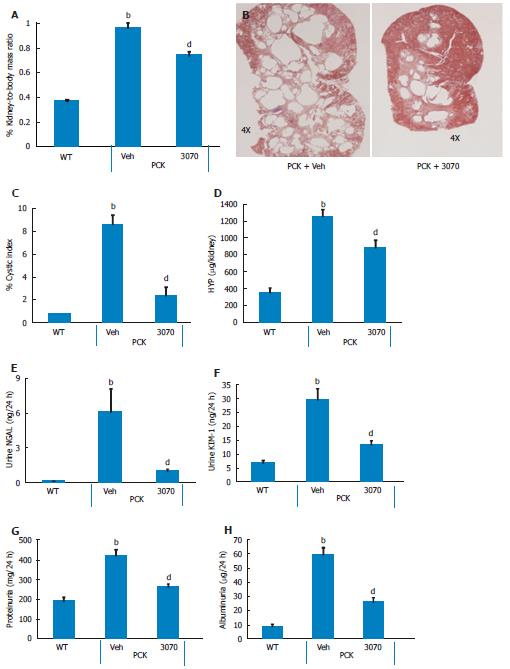
Figure 2 ANG3070 therapy attenuates renal mass, cystic index, renal injury, fibrosis and renal dysfunction.
A, C: By approximately 10 wk of age, PCK rats [vehicle (Veh) cohort] had significantly larger renal mass and renal-to-body mass ratio (A) and increased cystic index (C) compared to the age-matched WT cohort (bP < 0.01); B: Representative hematoxylin and eosin (HE)-stained renal sagittal sections (B) from PCK + Veh and a PCK + ANG3070 rats demonstrating cystic distribution across the renal parenchyma. Treatment of PCK rats with ANG3070 from weeks six to ten was associated with reduced kidney mass and kidney-to-body mass ratio (A) (dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh); C: Treatment with ANG3070 reduced renal cystic index (dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh); D: Total kidney hydroxproline (a marker of collagen) content was increased at week ten in the PCK (Veh) rat, treatment with ANG3070 was associated with a reduction in this marker of kidney fibrosis (bP < 0.01, vs WT; dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh); E, F: Compared to the WT cohort, PCK (Veh) rats exhibited renal injury evidenced by increased urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) (E) and urine kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) (F) (bP < 0.01, vs WT). Treatment with ANG3070 was associated with a reduction in these urinary markers (E and F) of renal injury; G, H: Renal dysfunction, evidenced by elevated proteinuria (G) and albuminuria (H) was reduced with ANG3070 treatment (dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh). HYP: Collagen marker.
- Citation: Paka P, Huang B, Duan B, Li JS, Zhou P, Paka L, Yamin MA, Friedman SL, Goldberg ID, Narayan P. A small molecule fibrokinase inhibitor in a model of fibropolycystic hepatorenal disease. World J Nephrol 2018; 7(5): 96-107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v7/i5/96.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v7.i5.96