Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
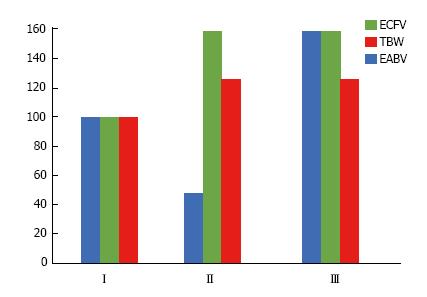
Figure 5 Percent changes from normal of body fluid compartments in hypervolemic states.
I: Normal body fluid state; II: Congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome with underfill mechanism of fluid retention; III: Nephrotic syndrome with overfill mechanism of fluid retention. EABV: Effective arterial blood volume; ECFV: Extracellular fluid volume; TBW: Total body water.
- Citation: Roumelioti ME, Glew RH, Khitan ZJ, Rondon-Berrios H, Argyropoulos CP, Malhotra D, Raj DS, Agaba EI, Rohrscheib M, Murata GH, Shapiro JI, Tzamaloukas AH. Fluid balance concepts in medicine: Principles and practice. World J Nephrol 2018; 7(1): 1-28
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v7/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v7.i1.1