Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Nephrol. May 6, 2015; 4(2): 196-212
Published online May 6, 2015. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i2.196
Published online May 6, 2015. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i2.196
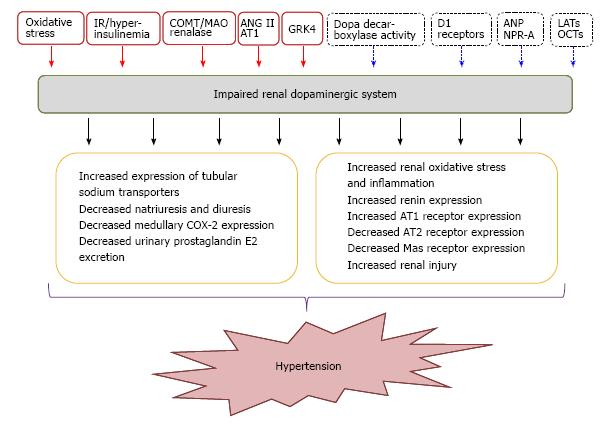
Figure 2 Impaired renal dopaminergic system and its association with hypertension.
Red full squares and arrows indicate those factors that promote the impairment of renal dopamine; blue dotted squares and arrows indicate those factors that enhance renal dopaminergic system. IR: Insulin-resistance; COMT: Catechol-O-methyl-transferase; MAO: Monoamine-oxidase: AT1: Angiotensin II receptor subtype 1; AT2: Angiotensin II receptor subtype 2; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase type 2; ANP: Atrial natriuretic peptide; NPR-A: Natriuretic peptide receptor type A; LATs: L-aminoacids transporters; OCTs: Organic cationic transporters; GRK4: G-protein receptor kinase 4.
- Citation: Choi MR, Kouyoumdzian NM, Rukavina Mikusic NL, Kravetz MC, Rosón MI, Rodríguez Fermepin M, Fernández BE. Renal dopaminergic system: Pathophysiological implications and clinical perspectives. World J Nephrol 2015; 4(2): 196-212
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v4/i2/196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v4.i2.196