Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Nephrol. Jun 25, 2025; 14(2): 101419
Published online Jun 25, 2025. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i2.101419
Published online Jun 25, 2025. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i2.101419
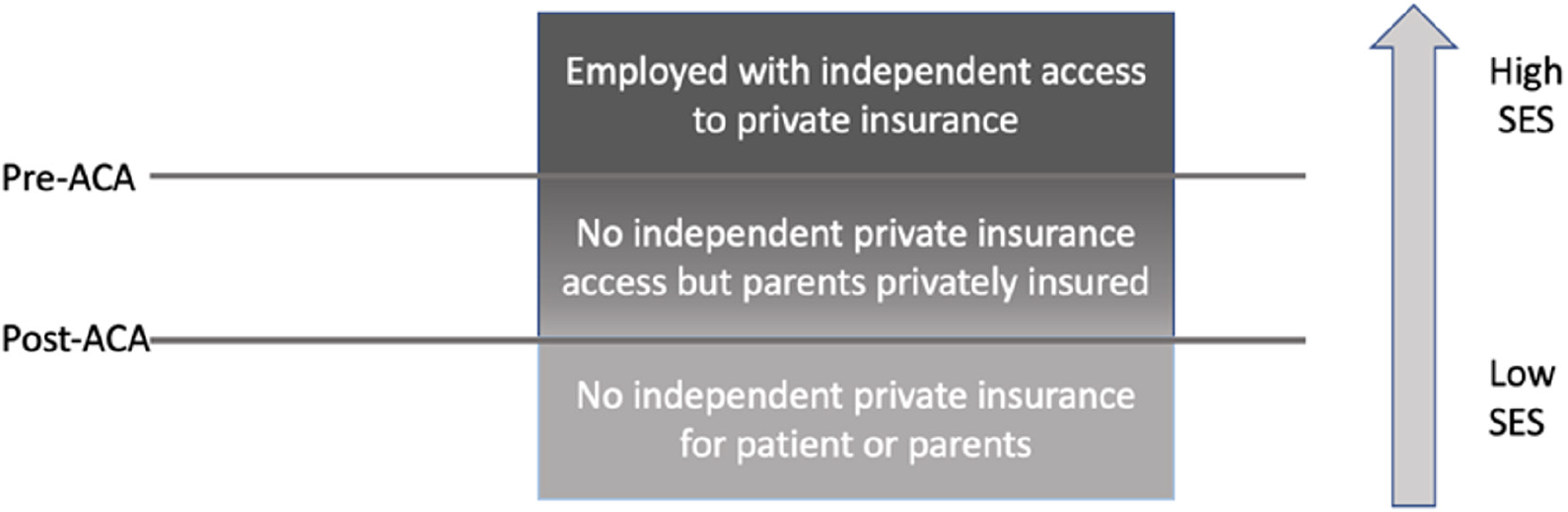
Figure 2 Conceptual diagram of proposed mechanism of study findings.
We hypothesize that the fall in living donor kidney transplantation rates among candidates with either private insurance or other insurance types is attributable to confounding by socioeconomic status, whereby candidates with intermediate socioeconomic status (i.e. those with access to parental private insurance) moved from public insurance to private insurance, thus lowering the group-level socioeconomic status of both privately insured candidates and non-privately insured candidates. ACA: Affordable Care Act; SES: Socioeconomic status.
- Citation: Perry K, Yu M, Adler JT, Maclay LM, Cron DC, Mohan S, Husain SA. Association between private insurance and living donor kidney transplant: Affordable Care Act as a natural experiment. World J Nephrol 2025; 14(2): 101419
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v14/i2/101419.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v14.i2.101419