Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
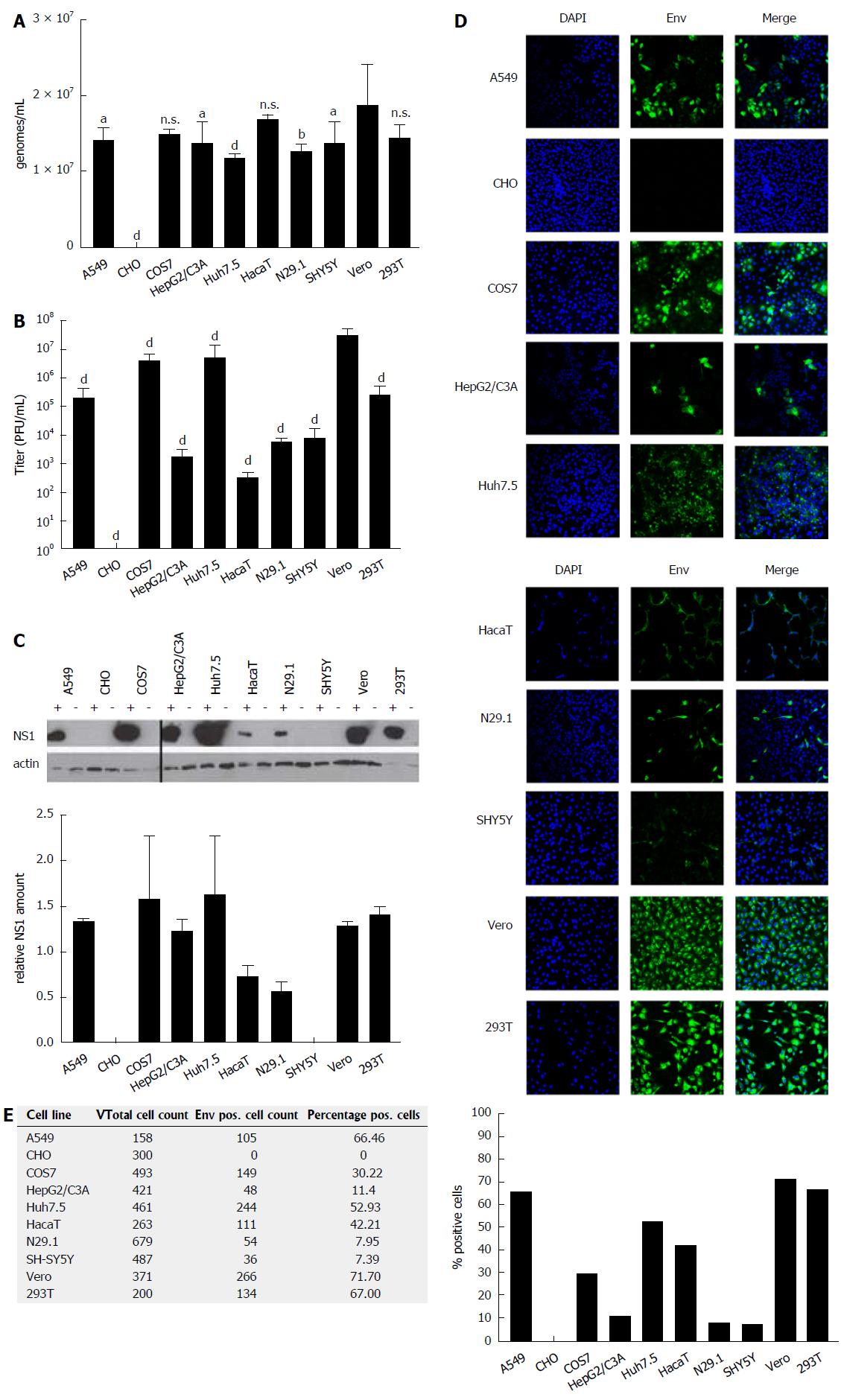
Figure 1 ZIKV-infected cells differ significantly with respect to the intracellular amount of infectious viral particles.
A: Cells were infected with an identical MOI of 0.1, using ZIKV Polynesia strain. Forty-eight hours after infection the intracellular amount of ZIKV-specific genomes was determined by RT-PCR. The data are the mean from four independent experiments. Amounts of Zika genomes are calculated using a Zika virus standard. A threshold value of 10 viral genomes was used. The bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. Statistical analysis was done by using 2-way ANOVA with Vero cells as reference value. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.0001; B: Cells were infected with an identical MOI of 0.1, using ZIKV Polynesia strain. Forty-eight hours after infection the cells were lysed and intracellular amount of infectious viral particles was determined by plaques assay using Vero cells. The data are the mean from four independent experiments. A threshold value of 10 plaques was used. The bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. Statistical analysis was done by using 2-way ANOVA with Vero cells as reference value. dP < 0.0001; C: Cells were infected with an identical MOI of 0.1, using ZIKV Polynesia strain. Forty-eight hours after infection the cells were lysed and intracellular amount of NS1 was determined by western blot analysis and referred to the amount of actin. The experiment was done in triplicate; one representative experiment is shown. Two different western blots from two independent experiments were quantified using Image J software. The relative NS1 amount represents the ratio between NS1 and actin; D: Cells were grown on cover slips and infected with an identical MOI of 0.1 using ZIKV Polynesia strain. Forty-eight hours after infection the cells were fixed by ethanol. To quantify the intracellular amount of ZIKV envelope protein and to analyze the subcellular distribution of the envelope protein in the different cell lines, confocal immunofluorescence microscopy was performed using an envelope-specific antibody (green fluorescence). Nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue fluorescence). The pictures were taken at 450-fold magnification; E: In two visual fields the total number of cells was determined by counting the number of DAPI-labeled cells. For quantification of ZIKV-positive cells immunofluorescence microscopy was performed using the envelope protein specific antibody 4G2. The percentage of ZIKV-positive cells was calculated and depicted in a diagram. ZIKV: Zika virus.
- Citation: Himmelsbach K, Hildt E. Identification of various cell culture models for the study of Zika virus. World J Virol 2018; 7(1): 10-20
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v7/i1/10.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v7.i1.10