Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
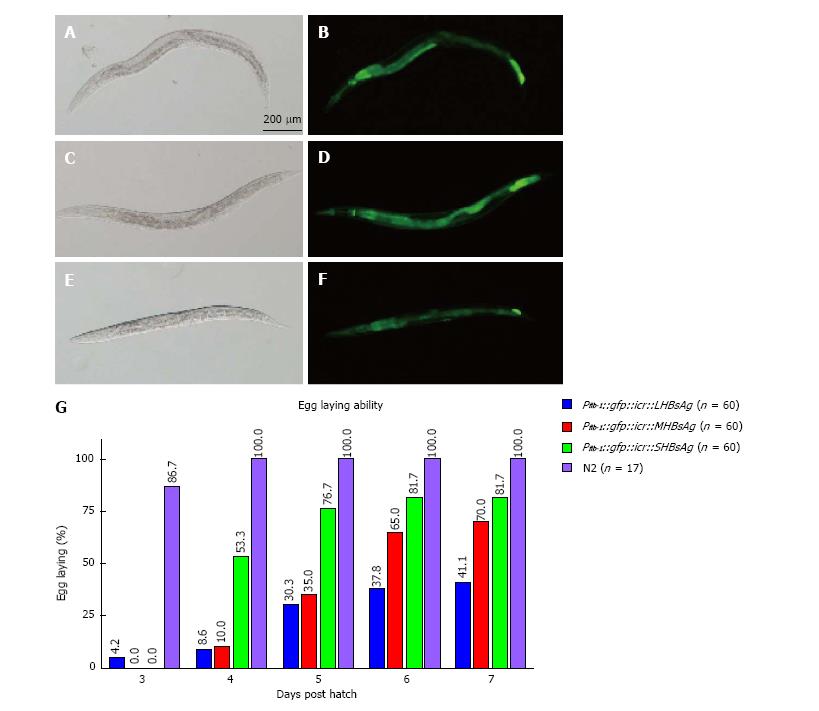
Figure 1 Expression of various lengths of hepatitis B virus antigens in whole worms induced defects in the rate of egg-laying.
A-F: Micrographs of transgenic worms expressing LHBsAg (A and B), MHBsAg (C and D), and SHBsAg (E and F) were captured under a bright-field microscope (A, C, and E) and a fluorescence microscope (B, D, and F). The heads of the worms are shown toward the left. The scale bar indicates 200 μm. G: Egg-laying capability of three lines of transgenic worms and wild-type worms (N2) shown using various color bars. The rate of egg-laying in 3 to 7 d post-hatching is shown above the bar. HBsAgs: Hepatitis B virus antigens.
- Citation: Chen YY, Lee LW, Hong WN, Lo SJ. Expression of hepatitis B virus surface antigens induces defective gonad phenotypes in Caenorhabditis elegans. World J Virol 2017; 6(1): 17-25
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v6/i1/17.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v6.i1.17