Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Virol. Nov 12, 2016; 5(4): 144-154
Published online Nov 12, 2016. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v5.i4.144
Published online Nov 12, 2016. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v5.i4.144
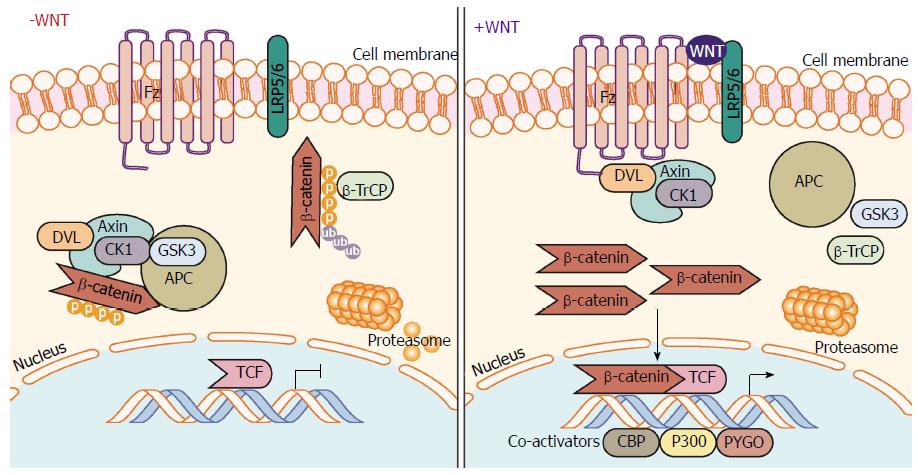
Figure 1 Canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
In the absence of Wnt ligand stimulation, the β-catenin destruction complex - consisting of the proteins Axin, CK1, GSK-3α/β, APC, and DVL - phosphorylate β-catenin allowing β-TrCP to ubiquitinate β-catenin marking it for proteasomal degradation. When stimulated by Wnt ligands, engagement of the Fz receptor and co-receptors LRP5/6, induces signaling through DVL inhibiting the action of the destruction complex. This frees β-catenin from degradation pathways allowing β-catenin to translocate and accumulate in the nucleus. β-catenin mediated interaction with TCF family transcription factors and co-activators (CBP, etc.) and initiates transcription of target genes. APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; β-TrCP: Beta-transducin repeat containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase; CBP: CREB-binding protein; CK1: Casein kinase 1; DVL: Dishevelled; Fz: Frizzled receptor; GSK-3: Glycogen synthase kinase 3; LRP: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein; TCF/LEF-1: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1.
- Citation: Zwezdaryk KJ, Combs JA, Morris CA, Sullivan DE. Regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by herpesviruses. World J Virol 2016; 5(4): 144-154
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v5/i4/144.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v5.i4.144