Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Virology. Aug 12, 2015; 4(3): 219-244
Published online Aug 12, 2015. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v4.i3.219
Published online Aug 12, 2015. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v4.i3.219
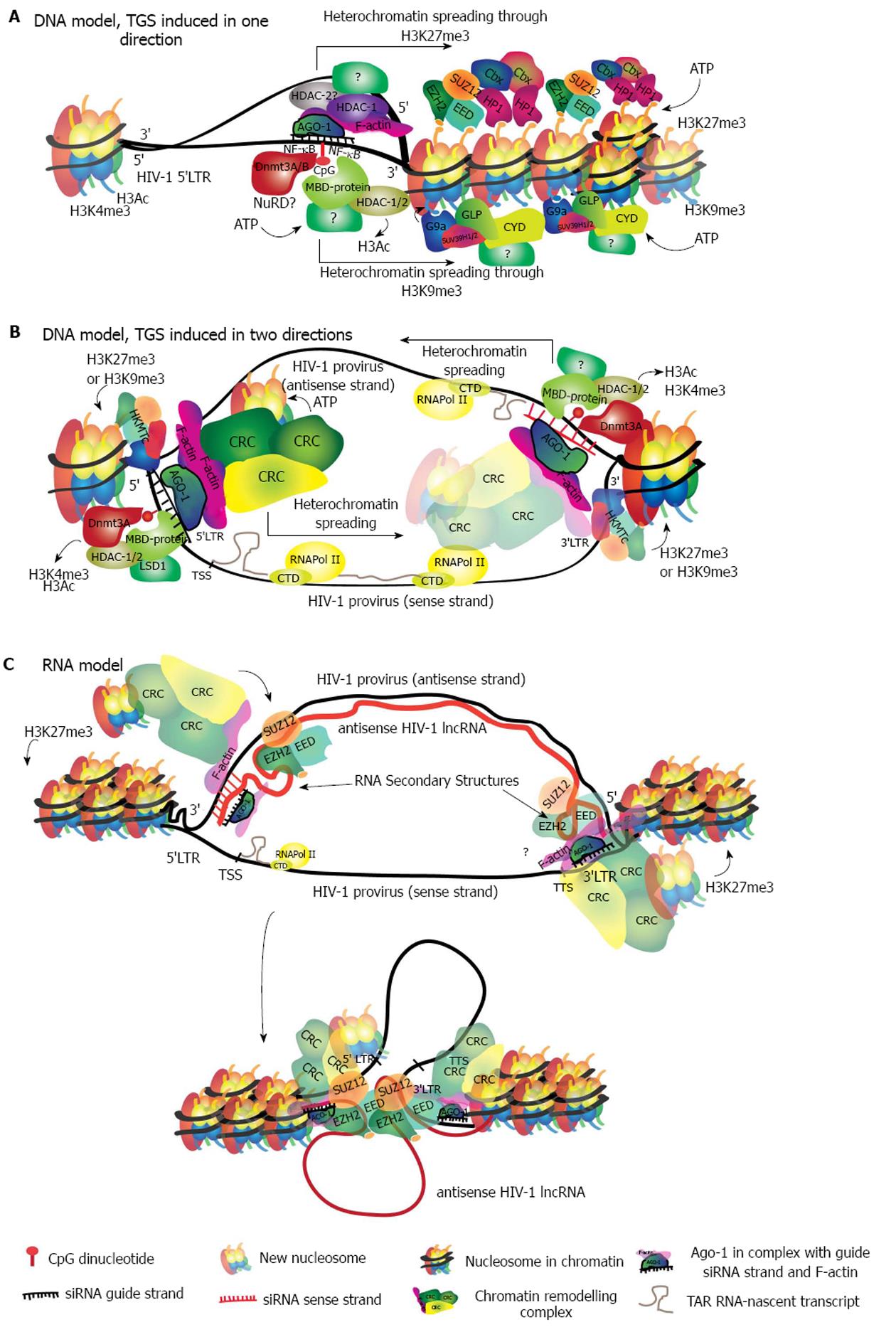
Figure 3 Models describing possible molecular mechanisms of siRNA-induced transcriptional gene silencing in human immunodeficiency virus 1.
A: DNA model in which the siRNA guide-strand finds its target in the 5’LTR promoter of the HIV-1 genome binding directly to the DNA. This binding triggers the recruitment of HDACs and HKMTs, which further recruit CRCs to induce chromatin compaction. Two mutually exclusive pathways are shown simultaneously, for simplicity. While both pathways may be initiated with the DNA methylation of CpG dinucleotides, they differ in the proteins that are recruited to the locus. The pathway characterized by H3K27me3 is shown above and involves initial recruitment of PCR2 (EZH2-SUZ12-EED) followed by the specific CRCs readers of H3K27me3. The H3K9me3 recruits G9a or SUV39H1/2 followed by specific CRCs as well. In this model heterochromatin is likely to spread in only one direction; B: In this DNA model, both strands of the siRNA duplex find a target on opposite DNA strands given that both, the 5’LTR and 3’LTR from the HIV-1 genome, have the same sequence. Regardless of the epigenetic pathway that is induced, heterochromatin will spread in the 5’ to 3’ direction from each end of the HIV-1 genome; C: In the RNA binding model, antisense transcription generates a HIV-1 specific lncRNA that covers all the HIV-1 genome. The siRNA guide-strand will bind the 3’UTR of this transcript, which corresponds to the 5’LTR sequence. The binding recruits PCR2, which establishes H3K27me3 and may also interact with the secondary structures of the lncRNA. Higher order interactions may bring together the 3’end of the HIV-1 genome, recruiting CRCs and inducing heterochromatin. A binding site for the same siRNA strand remains in the DNA sense strand at the 3’LTR, which could potentially contribute to heterochromatin formation. HIV-1: Human immunodeficiency virus 1; DNMT3 A/B: DNA methyl-transferase A/B; HDAC: Histone deacetylase; MBD-protein: Methy-CpG-binding protein; Cbx: Chromobox family; HKMT: Histone lysine (K) methyl-transferase; CRC: Chromatin remodelling complex.
- Citation: Méndez C, Ahlenstiel CL, Kelleher AD. Post-transcriptional gene silencing, transcriptional gene silencing and human immunodeficiency virus. World J Virology 2015; 4(3): 219-244
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v4/i3/219.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v4.i3.219