Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Virol. Jun 25, 2024; 13(2): 89985
Published online Jun 25, 2024. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v13.i2.89985
Published online Jun 25, 2024. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v13.i2.89985
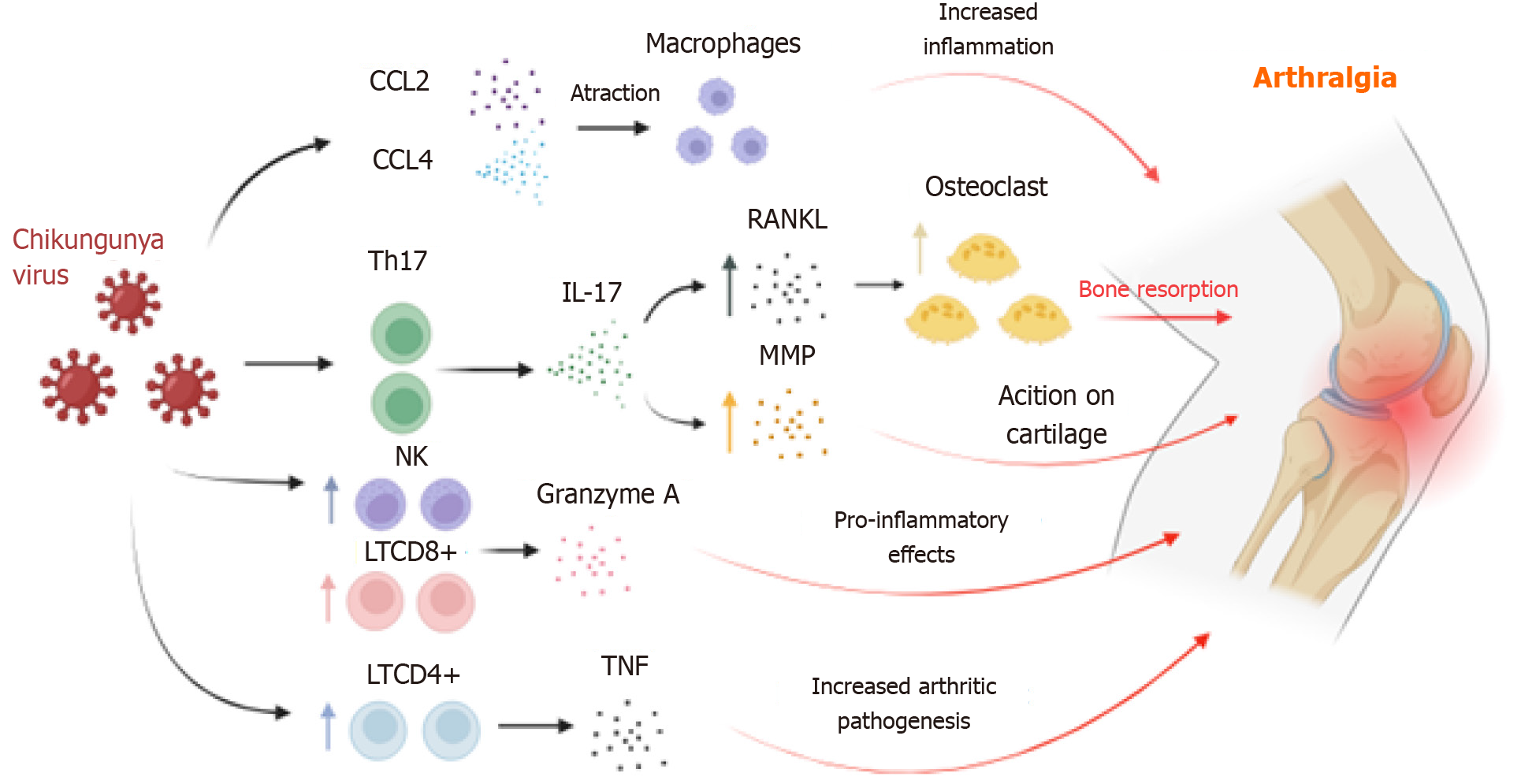
Figure 1 Supposed mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of arthritis caused by Chikungunya virus.
The elevation in levels of pro-inflammatory chemokines induces T helper type 17 response polarization, leading to interleukin-17 expression and subsequent increase in receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand. Granzyme A released by natural killer cells and CD8+ T cells targets type IV collagen, contributing to progressive joint damage. Th17: T helper type 17; CCL4: C-C motif ligand 4; NK: Natural killer; LTCD8: CD8 T lymphocytes; LTCD4: CD4 T lymphocytes; RANKL: Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinases; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Silveira-Freitas JEP, Campagnolo ML, dos Santos Cortez M, de Melo FF, Zarpelon-Schutz AC, Teixeira KN. Long chikungunya? An overview to immunopathology of persistent arthralgia. World J Virol 2024; 13(2): 89985
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v13/i2/89985.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v13.i2.89985