Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Virol. Sep 25, 2022; 11(5): 252-274
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.252
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.252
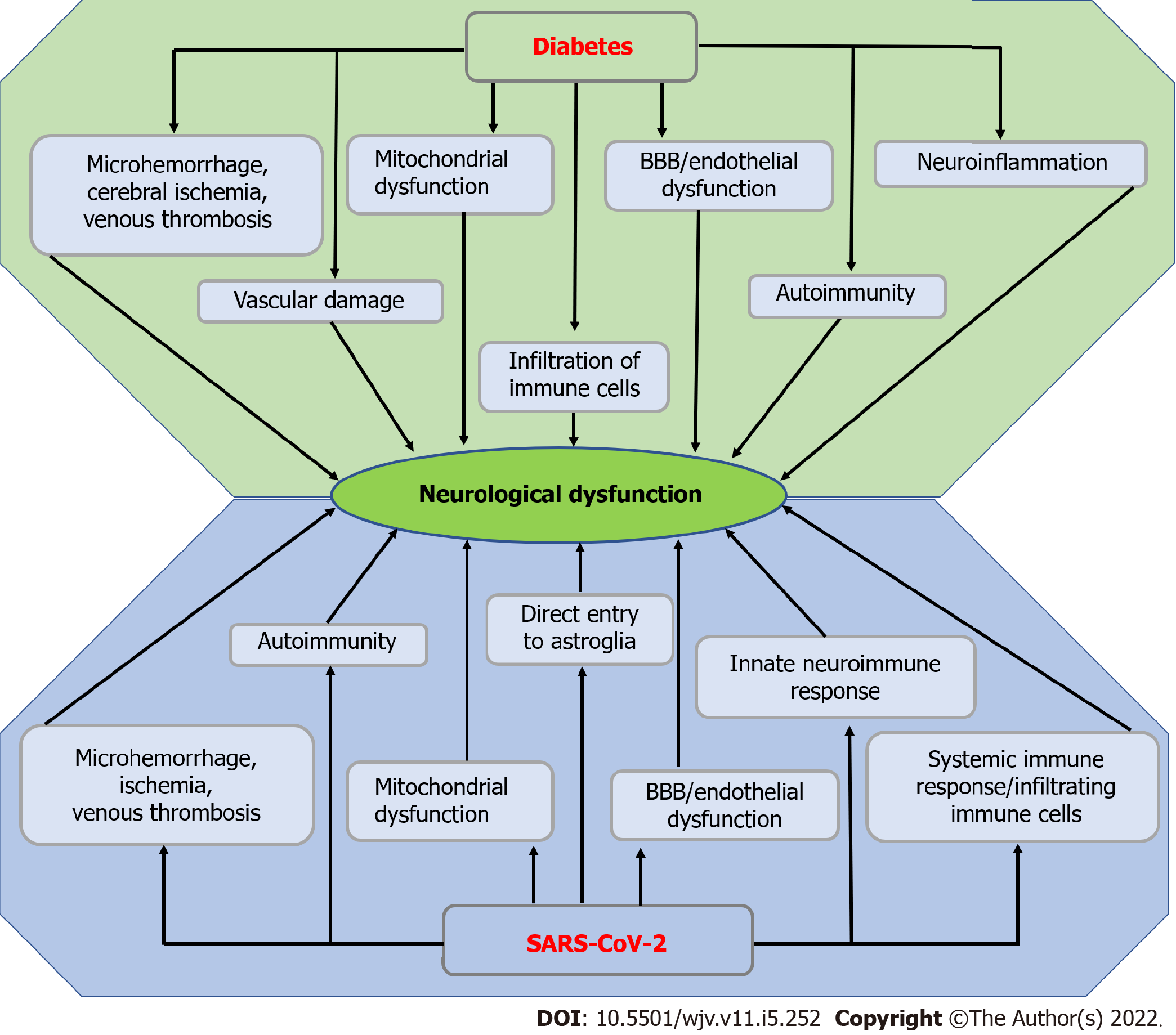
Figure 4 Possible mechanism of diabetes and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-induced neurological dysfunction.
Microhemorrhage, cerebral ischemia, venous thrombosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, endothelial or blood-brain barrier dysfunction, vascular damage, autoimmunity, infiltration of immune cells, and neuroinflammation in diabetes result in neurological dysfunction. On the other hand, microhemorrhage, ischemia, venous thrombosis, autoimmunity, mitochondrial dysfunction, endothelial or blood-brain barrier dysfunction, innate neuroimmune response, systemic immune response or infiltration of immune cells, and direct entry to astroglia lead to neurological dysfunction. BBB: Blood-brain barrier; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
- Citation: Roy B, Runa SA. SARS-CoV-2 infection and diabetes: Pathophysiological mechanism of multi-system organ failure. World J Virol 2022; 11(5): 252-274
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v11/i5/252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.252