Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Virol. Sep 25, 2022; 11(5): 252-274
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.252
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.252
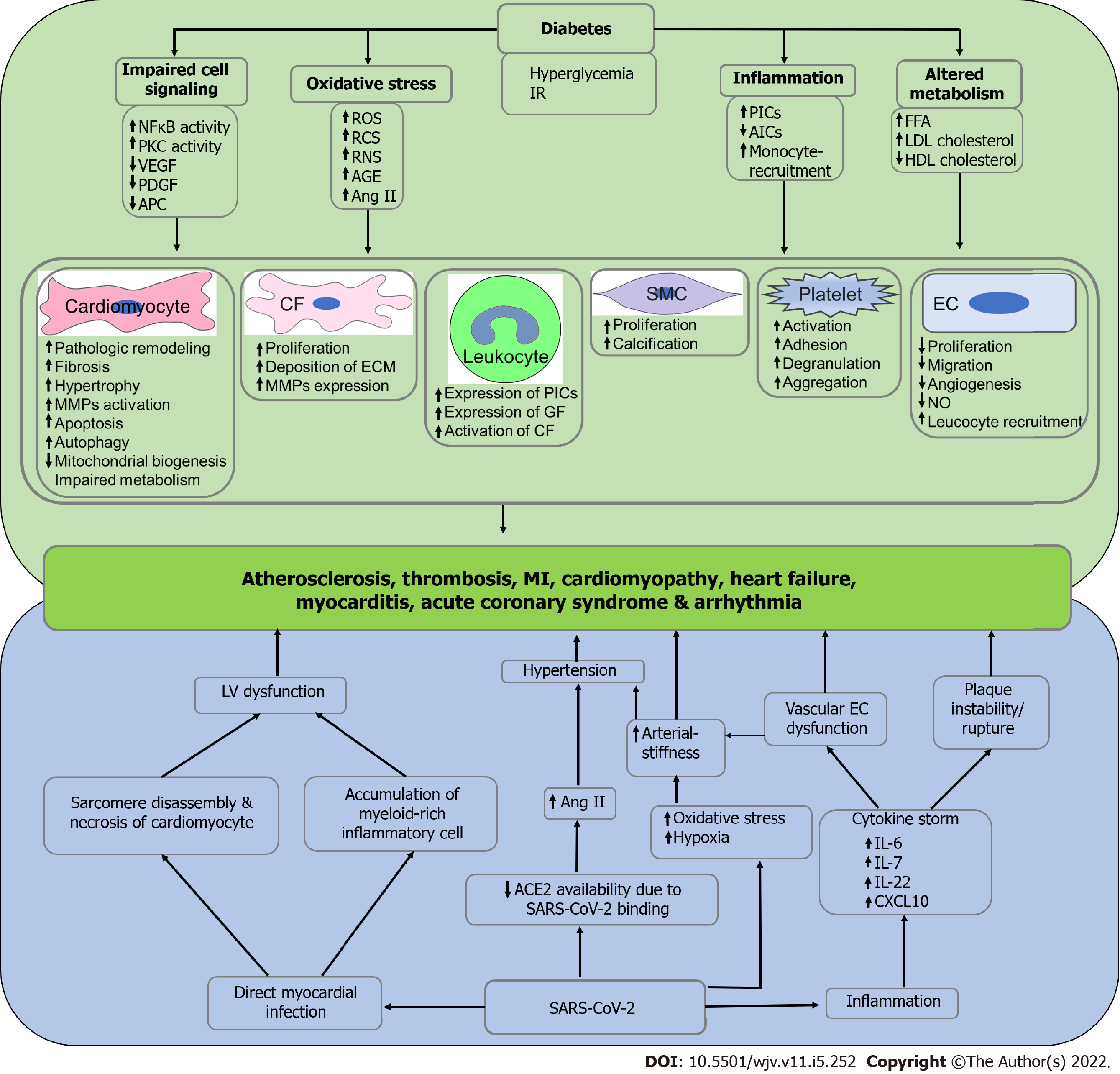
Figure 2 Possible mechanism of diabetes and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-induced cardiovascular complications.
Hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in diabetes is associated with impaired cell signaling, oxidative stress, inflammation, and altered metabolism and subsequently induce the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis, thrombosis, myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, myocarditis, acute coronary syndrome and arrhythmia due to impaired functioning of cardiomyocytes, cardiac fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells and endothelial cells, leukocytes, and platelets. On the other hand, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) directly infects the myocardium and subsequently induces left ventricular dysfunction due to sarcomere disassembly, necrosis of cardiomyocytes, and infiltration of myeloid-rich inflammatory cells. Additionally, SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces the availability of angiotensin converting enzyme-2 numbers, which results in elevated angiotensin II levels and subsequent manifestation of hypertension. SARS-CoV-2 infection is also associated with increased oxidative stress and hypoxia that may manifest hypertension due to arterial stiffness. Finally, inflammation in SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to cytokine storm and eventually induces vascular endothelial cell dysfunction and thrombotic plaque instability. Left ventricular dysfunction, hypertension, arterial stiffness, vascular endothelial cell dysfunction, and plaque instability induce the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases. IR: Insulin resistance; NFκB: Nuclear factor-κB; PKC: Protein kinase C; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; RNS: Reactive nitrogen species; RCS: Reactive carbonyl species; AGE: Advanced glycation end products; Ang II: Angiotensin II; PICs: Pro-inflammatory cytokines; AICs: Anti-inflammatory cytokines; FFA: Free fatty acid; LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; CF: Cardiac fibroblast; ECM: Extracellular matrix; GF: Growth factor; SMC: Smooth muscle cell; EC: Endothelial cell; NO: Nitric oxide; LV: Left ventricle; ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme-2; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-7: Interleukin-7; IL-22: Interleukin-22; CXCL10: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
- Citation: Roy B, Runa SA. SARS-CoV-2 infection and diabetes: Pathophysiological mechanism of multi-system organ failure. World J Virol 2022; 11(5): 252-274
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v11/i5/252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.252