Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Virol. Sep 25, 2022; 11(5): 237-251
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.237
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.237
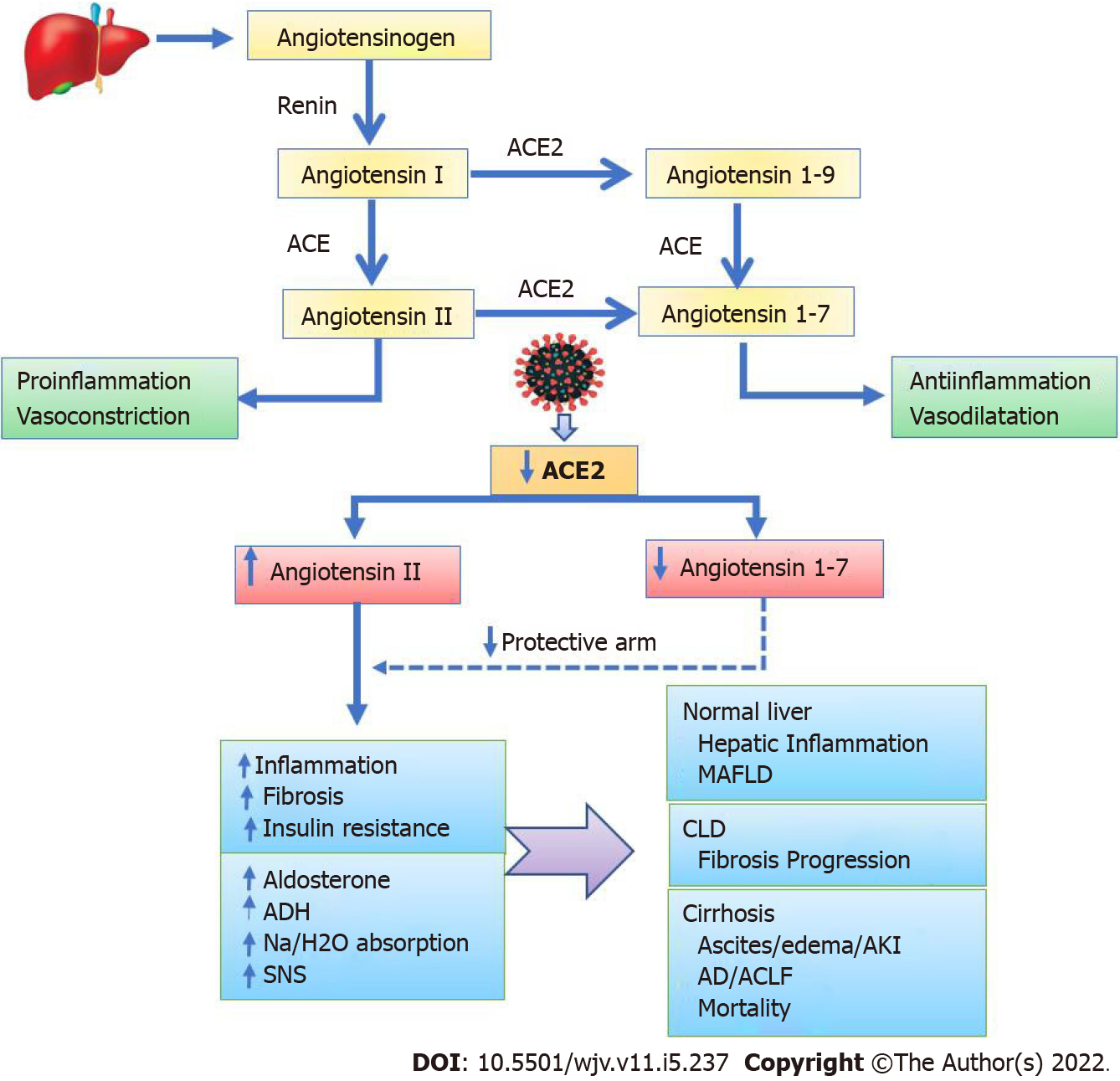
Figure 1 Interaction between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system system via angiotensin converting enzymes 2 as receptor.
The interaction between the cellular spike protein and angiotensin converting enzymes 2 (ACE2) allows severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 to enter host cells. ACE2 mediates alternative renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) pathways in the local RAAS system. ACE2 regulates the production of angiotensin 1–7 from angiotensin II (Ang II) and angiotensin 1–9. ACE2 after binding to virions is internalised, reducing its availability on the cellular surface. Once ACE2 is downregulated, Ang II gets upregulated which upon binding to the Ang II receptors, causes proinflammatory, profibrotic, vasoconstrictive, and antidiuretic responses. Overactivation of the RAAS has been linked to the development of refractory ascites, hepatorenal syndrome, and circulatory dysfunction in cirrhosis. SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; RAAS: renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzymes 2, CLD: Chronic liver disease, MAFLD: metabolic associated fatty liver disease, ADH: Antidiuretic hormone; Na: Sodium; H2O: Water; SNS: Sympathetic nervous system, AD: Acute decompensation, ACLF: Acute-on-chronic liver failure.
- Citation: Kumar R, Kumar V, Arya R, Anand U, Priyadarshi RN. Association of COVID-19 with hepatic metabolic dysfunction. World J Virol 2022; 11(5): 237-251
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v11/i5/237.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.237