Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Transplantation. Sep 10, 2018; 8(5): 156-166
Published online Sep 10, 2018. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v8.i5.156
Published online Sep 10, 2018. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v8.i5.156
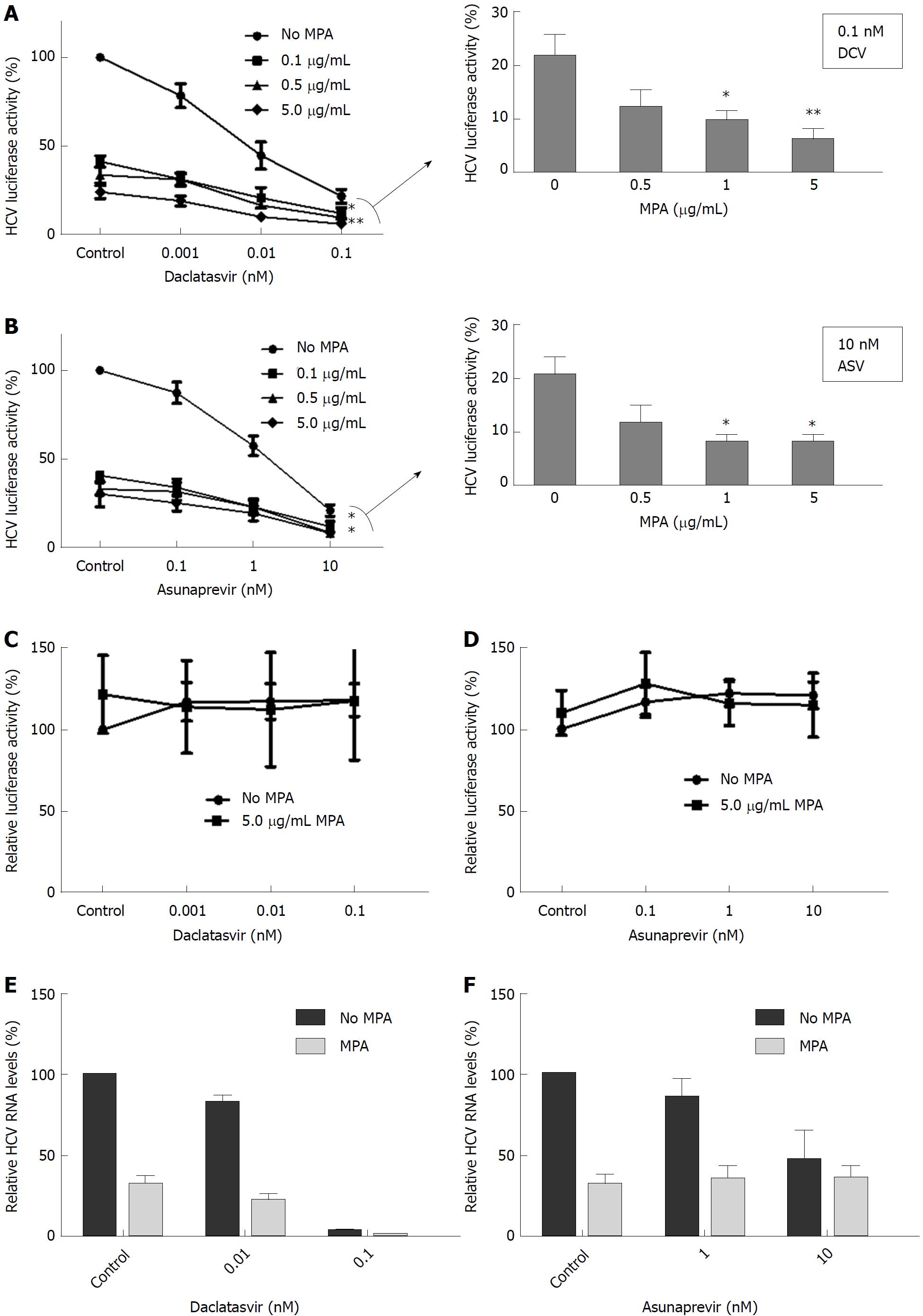
Figure 4 Daclatasvir and asunaprevir show a combined antiviral effect with mycophenolic acid.
A, B: Huh7-ETluc cells were cultured with increasing concentrations of DCV (A) or ASV (B), in combination with different concentrations of MPA. After 24 h incubation luciferase was measured. HCV replication was effectively inhibited by ASV and DCV and by increasing concentrations of MPA. As shown in the bar graphs, when cells were treated with 0.1 nmol/L DCV or 10 nmol/L ASV, the addition of 1 and 5 μg/mL MPA further significantly inhibited HCV replication (P = 0.02 for 1 μg/mL and P = 0.08 for 5 μg/mL MPA and 0.1 nmol/L DCV; P = 0.01 for 1 μg/mL, 5 μg/mL MPA and 10 nmol/L ASV, Mann-Whitney test). Results are means ± SEM of 4 or 5 independent experiments performed in triplicate; C, D: The luciferase signal in Huh7-PGK-luc cells, stably expressing luciferase, was not affected by any concentration of DCV (C) or ASV (D) with or without MPA, indicating that the observed effect in HUh7-ETluc is not due to non-specific inhibition of luciferase. Results are mean ± SE of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate; E: In the Huh7 infectious model, 5 μg/mL MPA reduced HCV replication by 68% of control levels. The inhibition of HCV replication by DCV was further reduced by MPA. The highest dose of DCV (0.1 nmol/L) inhibited HCV replication by 96.5% of control levels with an extra reduction by 99.4% of control levels by MPA; F: When HCV infected Huh7 cells were treated with 10 nmol/L ASV, HCV replication was reduced by 54% of control levels, with no additional effect of MPA. Results are mean of 6 experiments, performed in duplicate. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; DCV: Daclatasvir; ASV: Asunaprevir; MPA: Mycophenolic acid.
- Citation: de Ruiter PE, Gadjradj Y, de Knegt RJ, Metselaar HJ, Ijzermans JN, van der Laan LJ. Interaction of immunosuppressants with HCV antivirals daclatasvir and asunaprevir: combined effects with mycophenolic acid. World J Transplantation 2018; 8(5): 156-166
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v8/i5/156.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v8.i5.156