Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Transplant. Feb 24, 2018; 8(1): 23-37
Published online Feb 24, 2018. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v8.i1.23
Published online Feb 24, 2018. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v8.i1.23
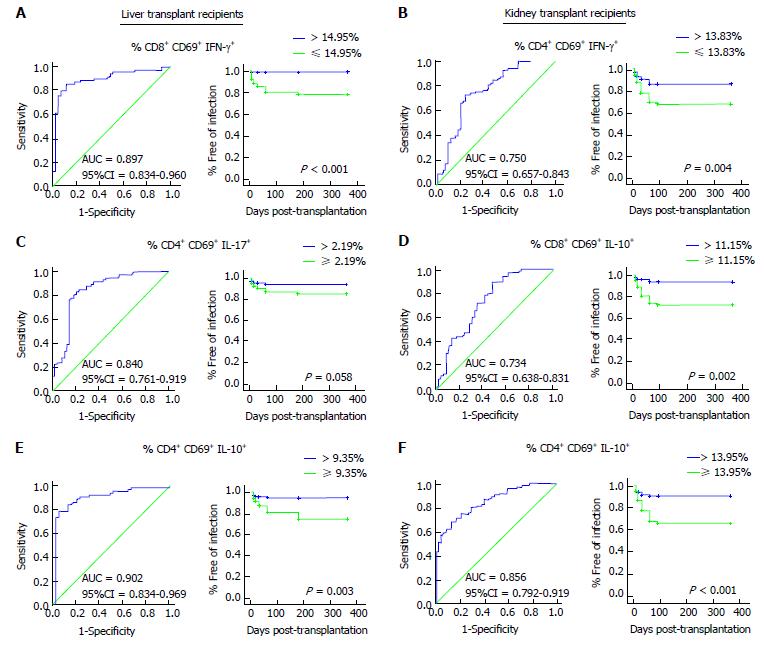
Figure 5 Post-transplantation receiver operating characteristic curve for the intracellular cytokine production capacity and the effect of the % of intracellular cytokine production capacity in stimulated T lymphocytes cut-off values for the discrimination of liver and kidney recipients likely to develop opportunistic infection between the 1st and 6th month post-transplantation (Kaplan–Meier analysis).
A: Post-transplant % of CD8+CD69+IFNγ+ in LTr; B: Post-transplant % of CD4+CD69+IFNγ+ in KTr; C: Post-transplant % of CD4+CD69+IL-17+ in LTr; D: Post-transplant % of CD8+CD69+IL-10+ in KTr; E: Post-transplant % of CD4+CD69+IL-10+ in LTr; F: post-transplant % of CD4+CD69+IL-10+ in KTr. LTr: Liver transplant recipients; KTr: Kidney transplant recipients.
- Citation: Boix F, Llorente S, Eguía J, Gonzalez-Martinez G, Alfaro R, Galián JA, Campillo JA, Moya-Quiles MR, Minguela A, Pons JA, Muro M. In vitro intracellular IFNγ, IL-17 and IL-10 producing T cells correlates with the occurrence of post-transplant opportunistic infection in liver and kidney recipients. World J Transplant 2018; 8(1): 23-37
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v8/i1/23.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v8.i1.23