Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Transplant. Dec 24, 2017; 7(6): 329-338
Published online Dec 24, 2017. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v7.i6.329
Published online Dec 24, 2017. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v7.i6.329
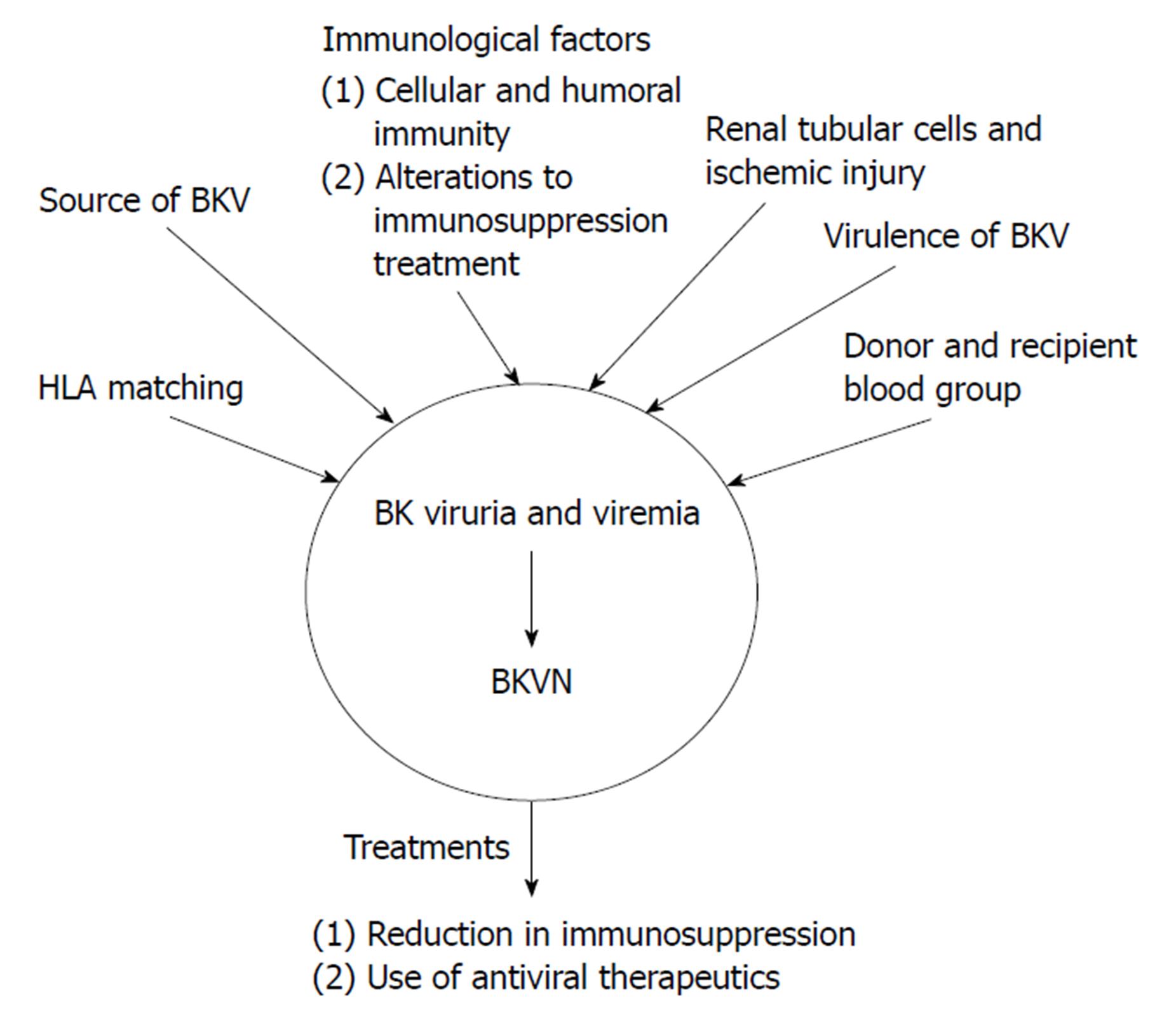
Figure 1 Proposed mechanisms for the pathogenesis of BK virus-associated nephritis after BK virus infection has occurred resulting in BK viruria or BK viremia.
These mechanisms include immunological factors, such as alterations to immunosuppressive therapy and cellular and humoral immunity, the source of BKV, either from the recipient or the donor, HLA matching, donor and recipient blood group. The two main treatment options for BKVN are a reduction in immunosuppression and the use of antiviral therapies. These treatments can also be used for BK viruria and viremia in order to prevent progression to BKVAN. BKV: BK virus; BKVAN: BK virus-associated nephritis.
- Citation: Scadden JR, Sharif A, Skordilis K, Borrows R. Polyoma virus nephropathy in kidney transplantation. World J Transplant 2017; 7(6): 329-338
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v7/i6/329.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v7.i6.329