Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Transplant. Dec 24, 2016; 6(4): 736-742
Published online Dec 24, 2016. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i4.736
Published online Dec 24, 2016. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i4.736
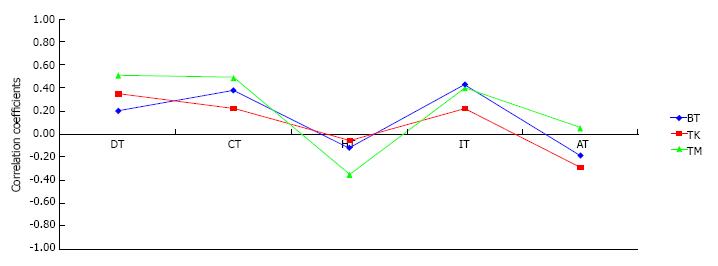
Figure 3 Correlations between temperament evaluation of memphis, pisa and san diego autoquestionnaire and basel assessment of adherence to immunosuppressive medication instrument.
BAASIS: Basel assessment of adherence to immunosuppressive medication instrument; DT: Depressive temperament; CT: Cyclothymic temperament; HT: Hyperthymic temperament; IT: Irritable temperament; AT: Anxious temperament; BT: BAASIS total score; TK: BAASIS taking dimension; TM: BAASIS timing dimension. Correlation coefficients (r) < 0.3 indicate weak correlation, ≤ 0.7 moderate correlation, > 0.7, strong correlation.
- Citation: De Pasquale C, Veroux M, Fornaro M, Sinagra N, Basile G, Gozzo C, Santini R, Costa A, Pistorio ML. Psychological perspective of medication adherence in transplantation. World J Transplant 2016; 6(4): 736-742
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v6/i4/736.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v6.i4.736