Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Transplant. Dec 24, 2016; 6(4): 719-728
Published online Dec 24, 2016. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i4.719
Published online Dec 24, 2016. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i4.719
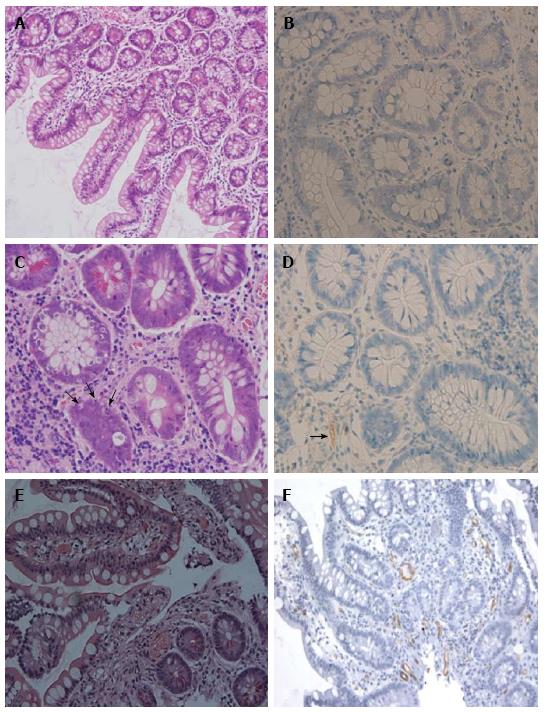
Figure 2 Histopatholgy of intestinal allograft.
A and B: No rejection: normal mucosal architecture of small bowel biopsy after transplantation. No staining for C4d is seen in the capillaries of the lamina propria; C and D: Acute cellular rejection (ACR): There is mononuclear infiltration, crypt epithelial injury, and apoptotic bodies (arrows) in the lamina propria. Weak and focal staining for C4d (arrows) is sometimes present in a patient with ACR; E and F: Acute antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR): There is prominent hemorrhage and congestion with scattered fibrin thrombin in the lamina propria. Widespread and bright staining for C4d is present in the capillaries of the lamina propria. Magnifications: × 200 in A, E and F; × 400 in B, C and D. A, C, E: H and E; B, D, F: C4d.
- Citation: Wu GS, Cruz Jr RJ, Cai JC. Acute antibody-mediated rejection after intestinal transplantation. World J Transplant 2016; 6(4): 719-728
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v6/i4/719.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v6.i4.719