Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Transplant. Sep 18, 2025; 15(3): 102383
Published online Sep 18, 2025. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v15.i3.102383
Published online Sep 18, 2025. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v15.i3.102383
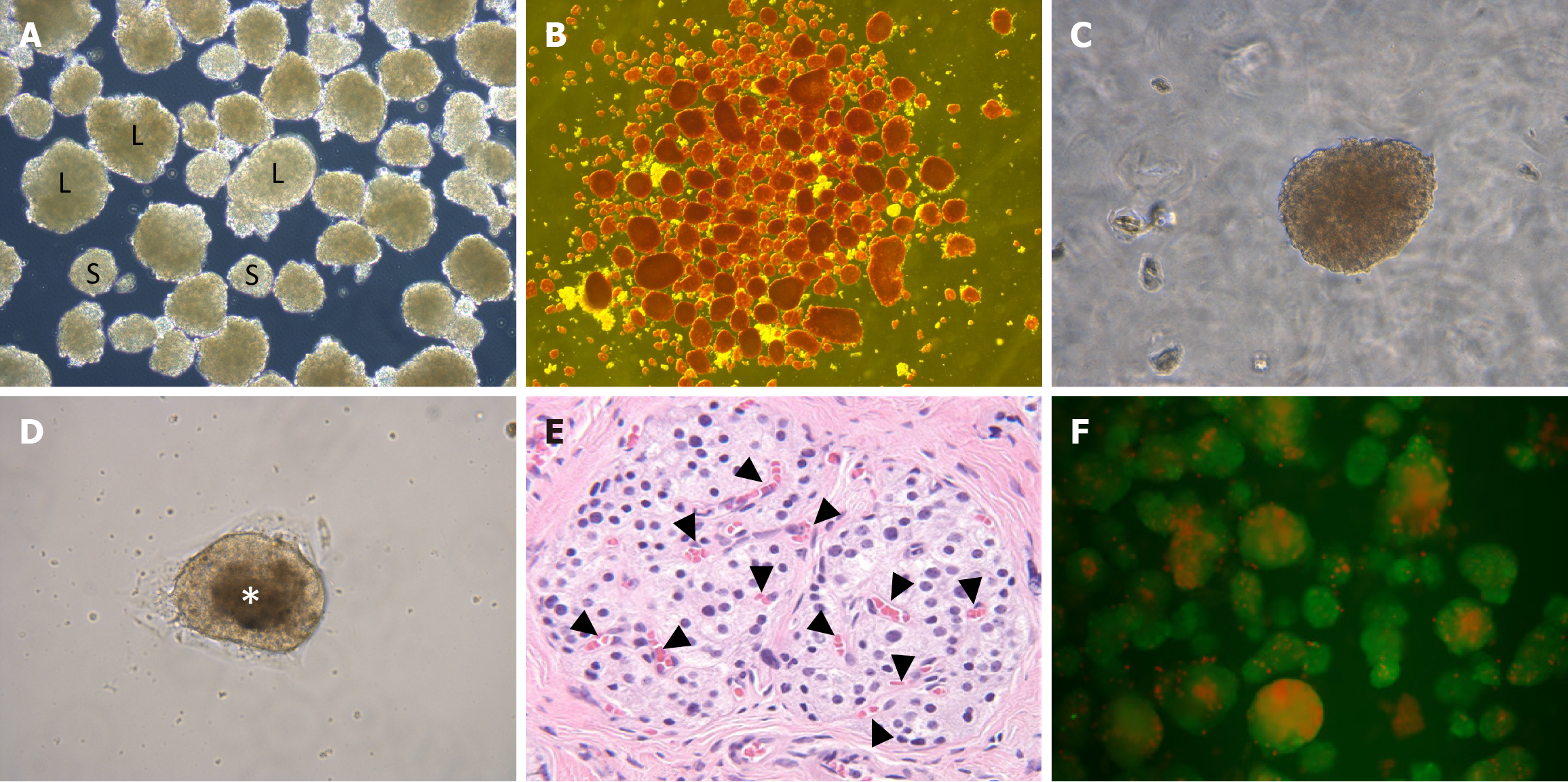
Figure 4 Isolated human islets at various stages of assessment before transplantation.
A: Unstained isolated human islets of different sizes (S: Small-sized islet; L: Large-sized islet); B: Dithizone (Diphenylthiocarbazone)-stained human islets, freshly isolated, showing the purity of the preparation; C: Unstained normal human islet under higher magnification; D: Unstained human islet with central necrosis after culture for 5 days, viewed under higher magnification; E: Haematoxylin and Eosin-stained image of large-sized islet in native pancreas with multiple intra-islet capillaries (black arrowhead) (higher magnification); F: Fluorescein diacetate/propidium iodide staining to assess the viability of the isolated islets (Bright green fluorescence indicates live cells, while bright red or orange fluorescence indicates dead or necrotic cells).
- Citation: Rout S, Mishra PR, Balamurugan AN, Ravi PK. Islet dimension and its impact on transplant outcome: A systematic review. World J Transplant 2025; 15(3): 102383
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v15/i3/102383.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v15.i3.102383