Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Transplant. Mar 18, 2025; 15(1): 99220
Published online Mar 18, 2025. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v15.i1.99220
Published online Mar 18, 2025. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v15.i1.99220
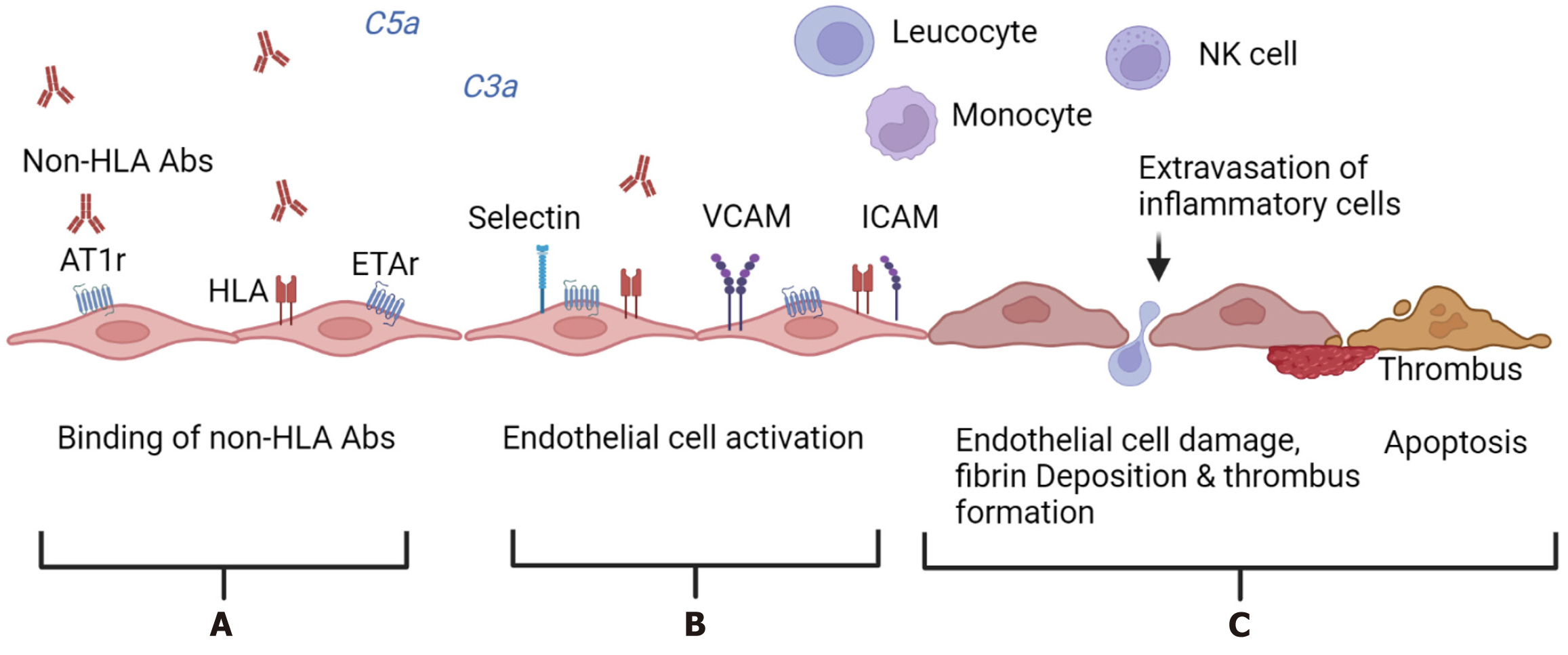
Figure 2 Mechanisms of action of non-human leucocyte antigen antibodies.
A: The targets of these antibodies are non-human leucocyte antigens (HLA) molecules expressed on endothelial cells. Non-HLA antibodies recognize various antigens such as angiotensin type 1 receptor and endothelin A receptor on endothelial cells and bind to them; B: This antibody binding to donor non-HLA antigens leads to complement-fixation and generation of anaphylatoxins (C3a and C5a) and recruitment of inflammatory cells. These antibodies can also activate the endothelial cells resulting in increased expression of HLA, non-HLA, and adhesion molecules such as intercellular adhesion molecule and vascular cell adhesion molecule; C: This results in damage to the endothelial cells, initiation of thrombogenesis, and induction of apoptosis of these cells, ultimately resulting in microvascular injury, thrombosis, and inflammation. HLA: Human leucocyte antigen; ICAM: Intercellular adhesion molecule; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule. This figure was created by BioRender.com (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Abbas K, Mubarak M. Expanding role of antibodies in kidney transplantation. World J Transplant 2025; 15(1): 99220
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v15/i1/99220.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v15.i1.99220