Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Transplant. Dec 18, 2023; 13(6): 379-390
Published online Dec 18, 2023. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v13.i6.379
Published online Dec 18, 2023. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v13.i6.379
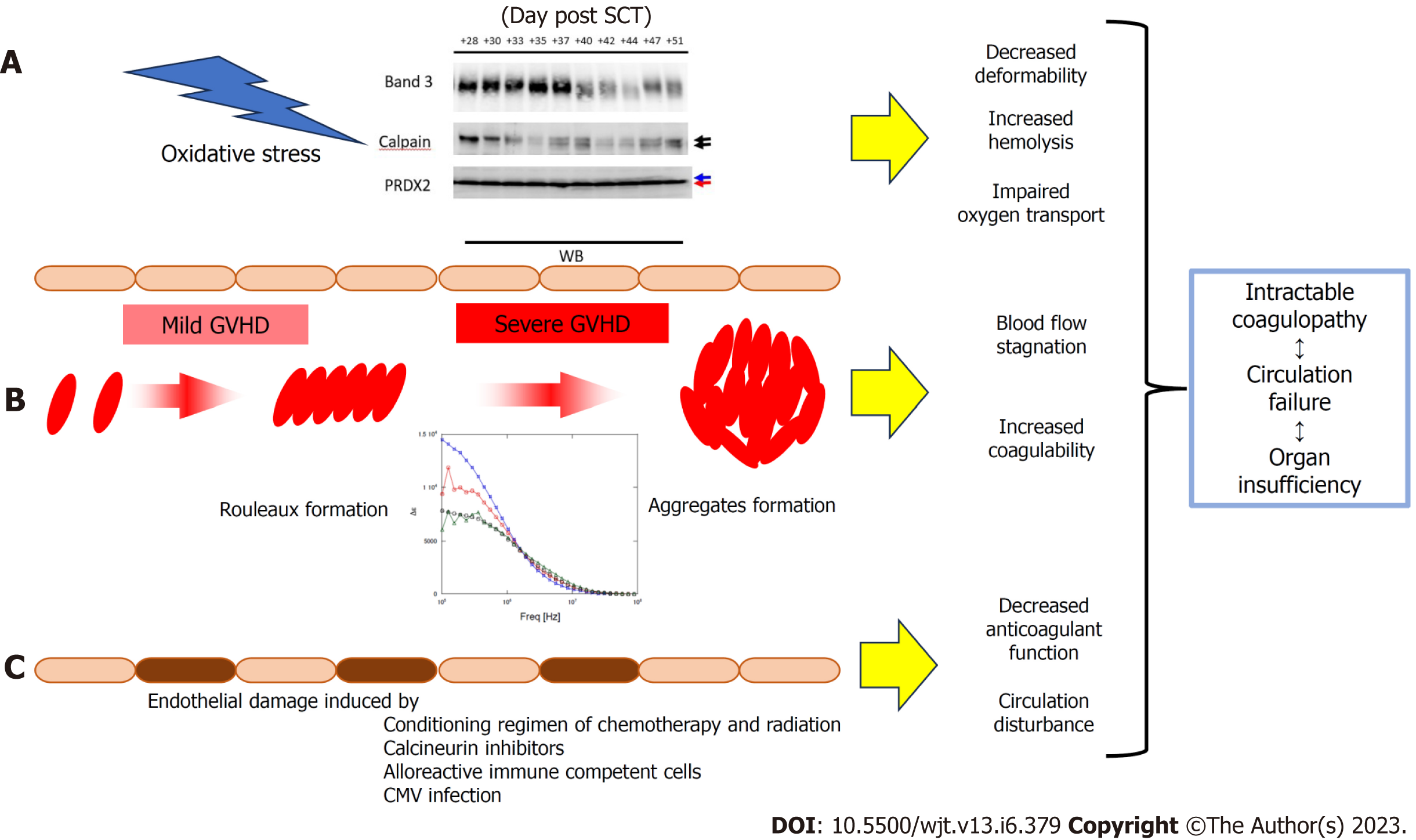
Figure 8 Schematic illustration of graft-versus-host disease from the perspective of dielectric analysis of whole blood cells.
A: In graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) of grade 3 or higher, oxidative stress-activated calpains lead to degradation of band3 and truncation of the C-terminus of PRDX2, leading to decreased erythrocyte plasticity, increased fragility, and impaired oxygen transport; B: Changes in plasma contents due to complex inflammation such as GVHD cause rouleaux formation and aggregation of erythrocytes, causing stasis in blood circulation and becoming more susceptible to coagulation activation; C: Vascular endothelial cell damage by pretreatment or calcineurin inhibitors is further prolonged and increased by alloimmune reactions and reactivation of cytomegalovirus virus, and the anticoagulant function of vascular endothelial cells is reduced. These phenomena are compounded and lead to refractory coagulopathy and subsequent organ circulatory failure and dysfunction. CMV: Cytomegalovirus; CRP: C-reactive protein; GVHD: Graft-versus-host disease; SCT: Stem cell transplantation.
- Citation: Nagasawa M. Pathophysiology of acute graft-versus-host disease from the perspective of hemodynamics determined by dielectric analysis. World J Transplant 2023; 13(6): 379-390
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v13/i6/379.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v13.i6.379