Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Transplant. Dec 18, 2023; 13(6): 379-390
Published online Dec 18, 2023. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v13.i6.379
Published online Dec 18, 2023. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v13.i6.379
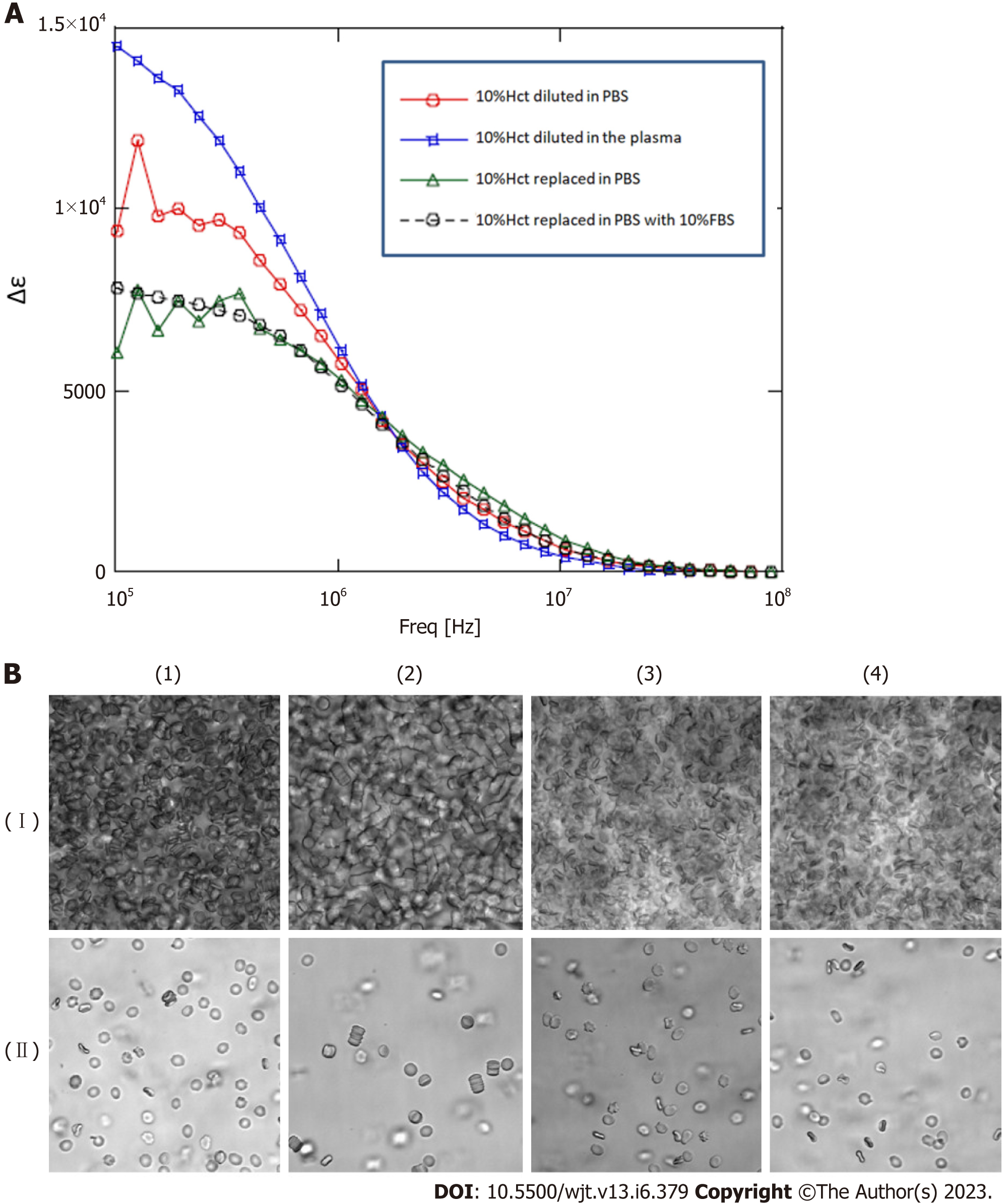
Figure 5 We conducted a replacement experiment for the blood cells and plasma components.
A: Blood sample (about 30%Hct) from the patient with graft-versus-host disease was diluted as 10%Hct diluted in phosphate buffer saline (PBS), 10%Hct diluted in the patient’s plasma, 10%Hct replaced in PBS, and 10%Hct replaced in PBS with 10%FBS, and dielectric properties were measured; B: (I) Blood sample (about 30%Hct) from the patient with graft-versus-host disease was diluted as (1) 10%Hct diluted in PBS, (2) 10%Hct diluted in the patient’s plasma, (3) 10%Hct replaced in PBS, and (4) 10%Hct replaced in PBS with 10%FBS, and observed by phase-contrast microscopy; (II) Sample of (I) was further diluted by 50-fold in the same way, and observed by phase-contrast microscopy. PBS: Phosphate buffer saline.
- Citation: Nagasawa M. Pathophysiology of acute graft-versus-host disease from the perspective of hemodynamics determined by dielectric analysis. World J Transplant 2023; 13(6): 379-390
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v13/i6/379.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v13.i6.379