Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Pharmacol. Sep 9, 2015; 4(3): 236-264
Published online Sep 9, 2015. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v4.i3.236
Published online Sep 9, 2015. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v4.i3.236
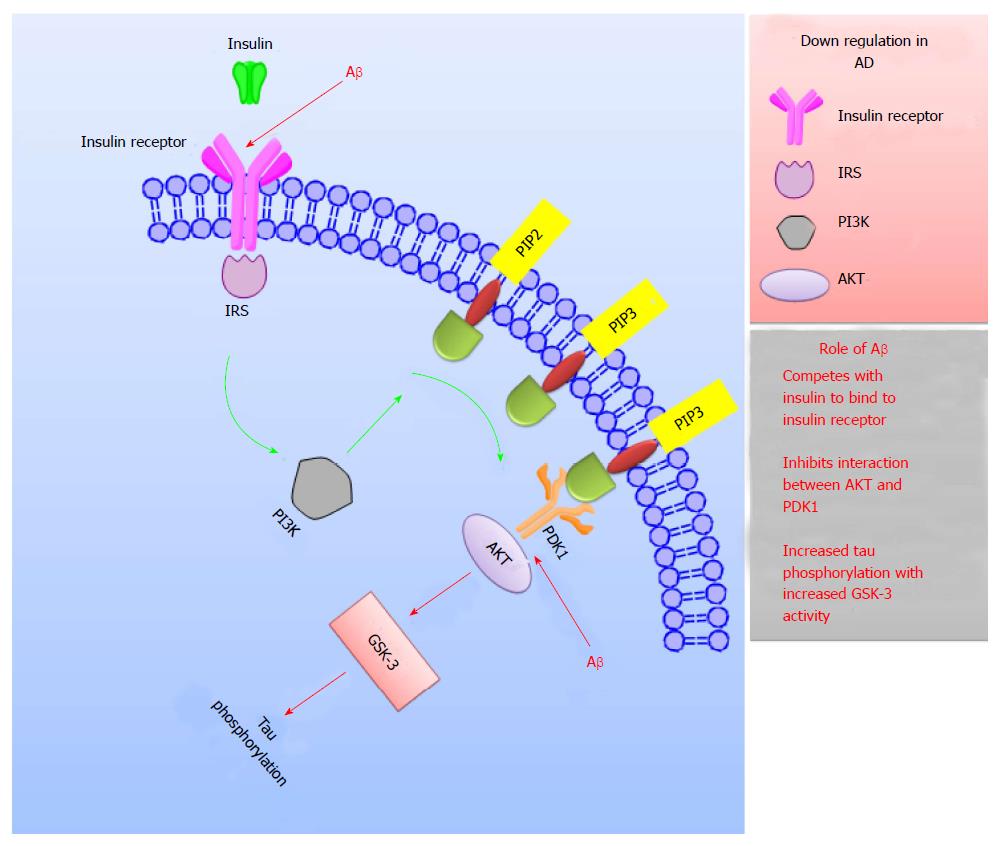
Figure 7 Schematic representation explaining the role of insulin in Alzheimer’s disease treatment.
Interaction of IRS with insulin receptor initiates the event of insulin signaling. This act triggers a cascade of activities which subsequently results in expression of PIP3 on the plasma membrane. This further leads to the activation of PDK-1 which interacts with AKT to generate the transmission of the insulin signal. In AD, the crucial components for insulin signaling like insulin receptors, IRS, PI3K and AKT; are down regulated. Also, Aβ competes with insulin to bind to insulin receptors, inhibits the PI3K-AKT interaction and enhances the GSK-3 activity which subsequently increases tau phosphorylation leading to impaired signaling in AD. IRS: Insulin receptor substrate; PI3K: Phosphoinositide-3-kinase; PIP: Phosphatidylinositol phosphate; PDK1: Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; AKT: Protein kinase B; GSK-3: Glycogen synthase kinase-3; AD: Alzheimer’s disease.
- Citation: Desai P, Shete H, Adnaik R, Disouza J, Patravale V. Therapeutic targets and delivery challenges for Alzheimer’s disease. World J Pharmacol 2015; 4(3): 236-264
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v4/i3/236.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v4.i3.236