Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Pharmacol. Sep 9, 2015; 4(3): 236-264
Published online Sep 9, 2015. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v4.i3.236
Published online Sep 9, 2015. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v4.i3.236
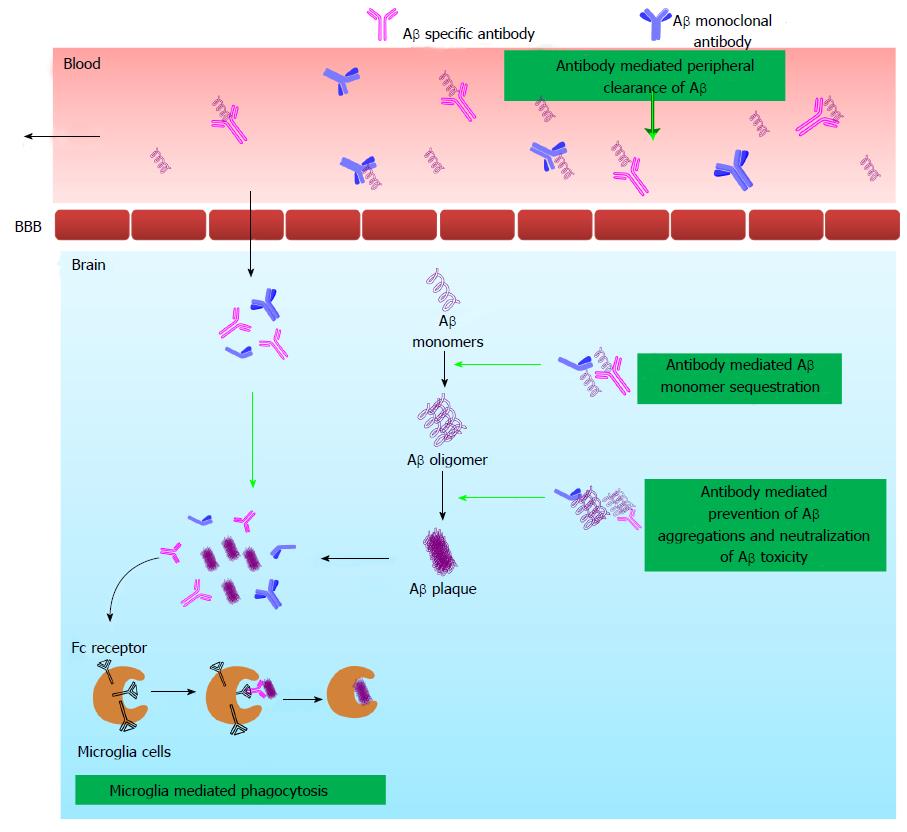
Figure 4 Schematic diagram explaining different mechanistic pathways hypothesized for immunotherapy to exert Amyloid β clearance from brain and plasma.
Immunotherapy exerts its activity by active and passive ways. In active immunization, the Aβ peptide or fragment is injected into the host which in turn stimulates cellular and humoral immune response to generate anti-Aβ antibody. In passive immunization, directly Aβ peptide specific antibody is injected into the host. The generated anti-Aβ antibodies provoke anti-AD activity by one of the or combination of following ways: microglia-mediated phagocytosis, antibody mediated Aβ monomer sequestration, antibody mediated prevention of Aβ aggregation and neutralization of Aβ toxicity and antibody mediated peripheral clearance of Aβ. Aβ: Amyloid β; BBB: Blood brain barrier. AD: Alzheimer’s disease.
- Citation: Desai P, Shete H, Adnaik R, Disouza J, Patravale V. Therapeutic targets and delivery challenges for Alzheimer’s disease. World J Pharmacol 2015; 4(3): 236-264
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v4/i3/236.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v4.i3.236