Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Pharmacol. Mar 9, 2015; 4(1): 96-116
Published online Mar 9, 2015. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v4.i1.96
Published online Mar 9, 2015. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v4.i1.96
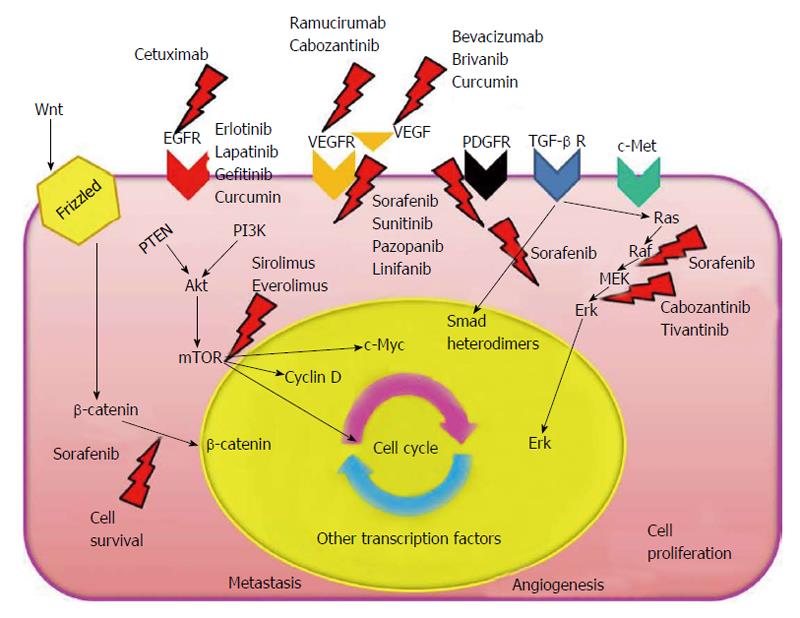
Figure 1 Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenetic pathways.
Main molecular targets of the major anti-tumoral drugs are indicated. VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; Erk: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptors; PDGFR: Platelet-derived growth factor receptors; TGF-β R: TGF-β receptor; RAS: Rat Sarcoma; RAF: Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; c-Myc: Myelocytomatosis cellular oncogene; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homology; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
- Citation: Cuestas ML, Oubiña JR, Mathet VL. Hepatocellular carcinoma and multidrug resistance: Past, present and new challenges for therapy improvement. World J Pharmacol 2015; 4(1): 96-116
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v4/i1/96.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v4.i1.96