Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Pharmacol. Dec 22, 2023; 12(4): 35-52
Published online Dec 22, 2023. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v12.i4.35
Published online Dec 22, 2023. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v12.i4.35
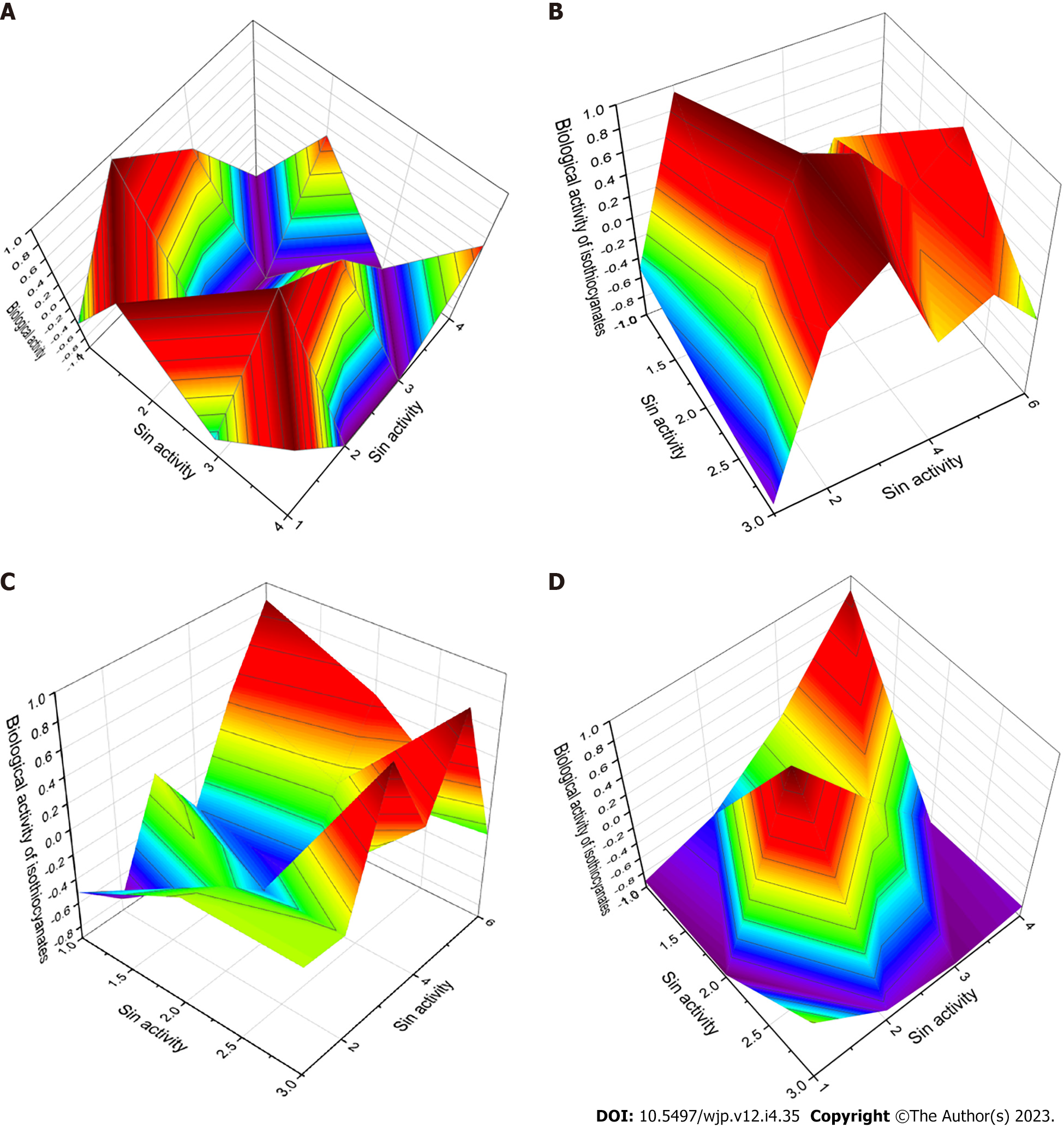
Figure 8 3D graphs.
A: 3D graph shows a wide range of biological activities and predicted pharmacological activities of benzyl isothiocyanate (9). This compound is characterized as an agonist of apoptosis. In addition, it exhibits antitumor properties and is an inhibitor of the development of the Gram-negative microaerophilic helical bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). The H. pylori infection is known to be an important public health problem worldwide, with a prevalence of 45% to 84%. The H. pylori bacteria enter the digestive tract and can cause ulcers in the lining of the stomach or in the upper part of the small intestine, and patients can develop chronic gastritis, atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, stomach cancer, or peptic ulcer disease. Amoxicillin is commonly used to treat this infection, and it appears that isothiocyanates may be a potential drug for H. pylori infection; B: 3D graph shows the predicted and calculated biological activity of isothiocyanates (compound numbers: 2, 14, and 17) showing the highest degree of confidence. All presented natural isothiocyanates have a dominant activity as an apoptosis agonist with a confidence of more than 96%. The second activity that characterizes these isothiocyanates is chemoprotective; C: 3D graph shows the predicted and calculated anti-H. pylori activity of isothiocyanates (compound numbers: 5, 8, and 20) showing the highest degree of confidence, more than 82.2%; D: 3D graph shows the predicted and calculated activity of isothiocyanates against periodontitis (compound numbers: 26, 27, and 28) showing the highest degree of confidence, more than 73%.
- Citation: Hanuš L, Naor T, Gloriozova T, Dembitsky VM. Natural isothiocyanates of the genus Capparis as potential agonists of apoptosis and antitumor drugs. World J Pharmacol 2023; 12(4): 35-52
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v12/i4/35.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v12.i4.35