Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Med Genet. Aug 27, 2014; 4(3): 69-76
Published online Aug 27, 2014. doi: 10.5496/wjmg.v4.i3.69
Published online Aug 27, 2014. doi: 10.5496/wjmg.v4.i3.69
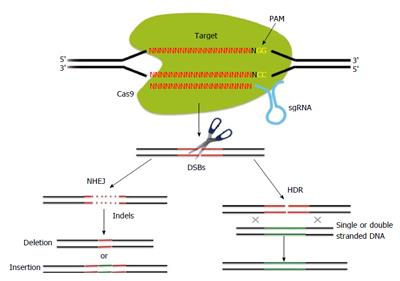
Figure 1 Schematic of the principles of clustered regularly at interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR associated (Cas)-mediated genome editing.
The CRISPR associated 9 (Cas9) endonuclease can generate sequence-specific double strand breaks (DSBs) of target DNAs bound to small guide RNAs (sgRNAs). The binding site of a target DNA requires a protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) (with the sequence NGG). DSBs generated by the Cas9 endonuclease are repaired by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR).
- Citation: Horii T, Hatada I. Genome engineering using the CRISPR/Cas system. World J Med Genet 2014; 4(3): 69-76
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3184/full/v4/i3/69.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5496/wjmg.v4.i3.69