Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Clin Infect Dis. Nov 25, 2017; 7(4): 50-57
Published online Nov 25, 2017. doi: 10.5495/wjcid.v7.i4.50
Published online Nov 25, 2017. doi: 10.5495/wjcid.v7.i4.50
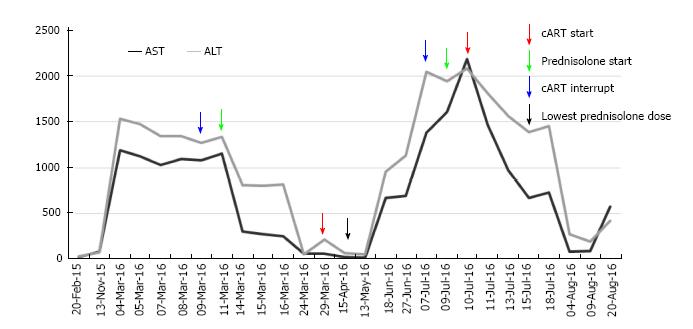
Figure 4 Transaminase values during follow-up.
Aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) values (UI/L) and their relationship with the interventions carried out and date (DD/MM): At the start of the follow-up, the patient was already receiving antiretroviral therapy, in the first interventions there is some confusion that does not allow to differentiate whether the decrease in serum transaminase levels was due to the onset of immunosuppressive therapy or the interruption of the antiretroviral therapy; also there is no indication to show if the second peak elevation of transaminases was due to the resumption of the antiretroviral therapy or due to the decrease in the dose of immunosuppressive therapy. In the end, it may be noted that, although the antiretroviral therapy was reset, the decline of transaminases continued with the immunosuppressive therapy, which helped to confirm the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. cART: Combination antiretroviral therapy.
- Citation: Noreña I, Morantes-Caballero JA, Garcés A, Gómez BJ, Rodríguez G, Saavedra C, Otero W. Autoimmune hepatitis in human immunodeficiency virus infection: Case report and literature review. World J Clin Infect Dis 2017; 7(4): 50-57
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3176/full/v7/i4/50.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5495/wjcid.v7.i4.50