Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Clin Infect Dis. Aug 25, 2012; 2(4): 54-62
Published online Aug 25, 2012. doi: 10.5495/wjcid.v2.i4.54
Published online Aug 25, 2012. doi: 10.5495/wjcid.v2.i4.54
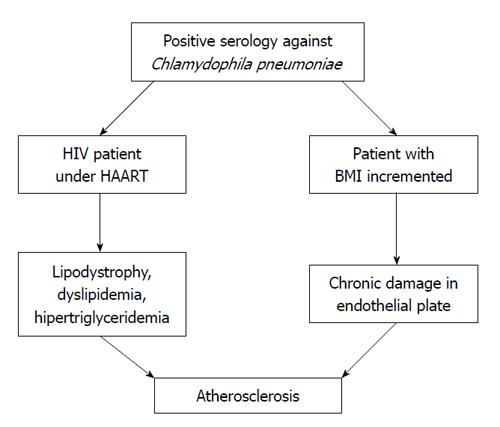
Figure 1 In the patient co infected with human immunodeficiency virus /chlamydia, under highly active antiretroviral therapy, a factor of risk can occur to develop lipodystrophy and other disorders of the metabolism of lipids as dyslipidemia or hipertriglyceridemia, conducting finally to atherosclerosis.
Thus same, in patients with re infections and obesity, would be able to occur an activation in the mechanism of inflammation that has an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis resulting in a cycle of inflammation, activation and continuous cell recruitment.
-
Citation: García-Elorriaga G, Rey-Pineda GD. Human immunodeficiency virus, atherosclerosis and
Chlamydophila pneumoniae . World J Clin Infect Dis 2012; 2(4): 54-62 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3176/full/v2/i4/54.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5495/wjcid.v2.i4.54