Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hypertens. Nov 23, 2013; 3(4): 27-31
Published online Nov 23, 2013. doi: 10.5494/wjh.v3.i4.27
Published online Nov 23, 2013. doi: 10.5494/wjh.v3.i4.27
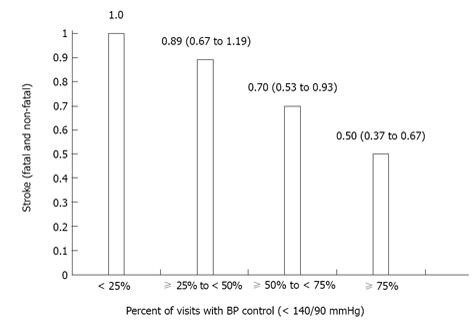
Figure 1 Reduction in the risk of fatal and non-fatal stroke according visits with blood pressure control in the International Verapamil SR-Trandolapril study[13].
Data expressed as hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) for each percentage of visits with blood pressure (BP) control (< 25% as the reference category).
- Citation: Pelegrí A, Arboix A. Blood pressure variability and cerebrovascular disease. World J Hypertens 2013; 3(4): 27-31
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3168/full/v3/i4/27.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5494/wjh.v3.i4.27