Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Exp Med. Jun 20, 2025; 15(2): 102285
Published online Jun 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i2.102285
Published online Jun 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i2.102285
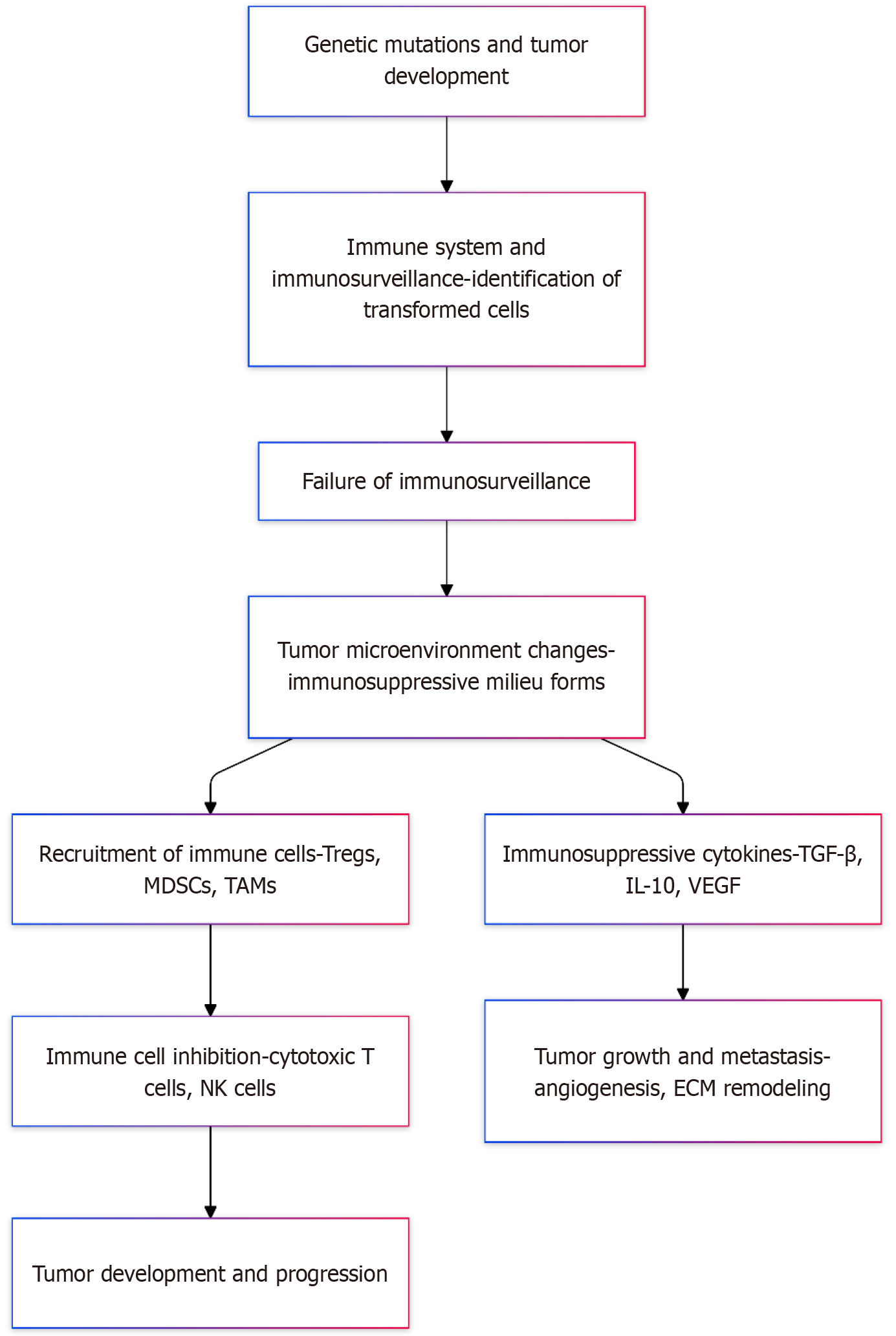
Figure 1 Immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment development and progression.
The flow from tumor development to progression involves several key steps. Genetic mutations lead to tumor formation. The immune system attempts immunosurveillance, identifying and eliminating transformed cells. When immunosurveillance fails, cancer cells survive and continue to grow. This failure creates an immunosuppressive microenvironment, driven by the recruitment of immune cells such as regulatory T cells, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and tumor-associated macrophages. These immune cells release immunosuppressive cytokines (transforming growth factor beta, interleukin-10, vascular endothelial growth factor), which inhibit cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells. As a result, tumor growth and metastasis are facilitated, including processes like angiogenesis and extracellular matrix remodeling. Ultimately, the tumor evades immune responses and progresses further. ECM: Extracellular matrix; IL: Interleukin; MDSCs: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; NK: Natural killer; TAMs: Tumor-associated macrophages; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; Tregs: Regulatory T cells; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Issa H, Singh L, Lai KS, Parusheva-Borsitzky T, Ansari S. Dynamics of inflammatory signals within the tumor microenvironment. World J Exp Med 2025; 15(2): 102285
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315x/full/v15/i2/102285.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v15.i2.102285