Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Exp Med. Jun 20, 2025; 15(2): 102175
Published online Jun 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i2.102175
Published online Jun 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i2.102175
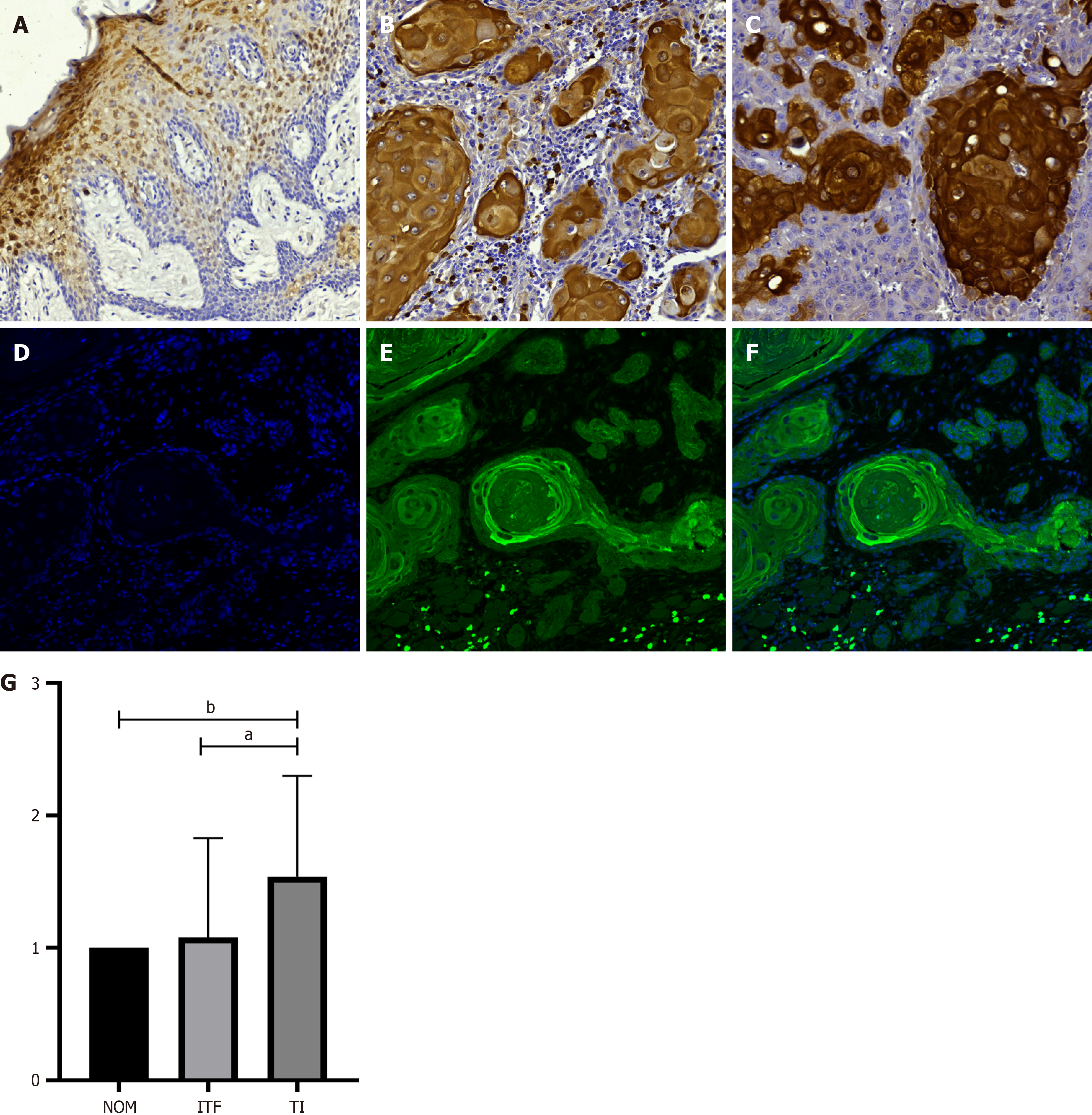
Figure 1 Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha.
A: Immunohistochemical expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) in the normal oral mucosa (NOM); B: Invasive tumor front (ITF); C: Tumor islands (TI). HIF-1α expression was significantly different between the TI and ITF regions (P = 0.0134). Additionally, a significant difference was observed between TI and NOM (P = 0.0115). (Immunohistochemistry, 20 × magnification); D: DAPI-stained nuclei (blue); E: HIF-1α expression (green); F: Merged image showing HIF-1α localization in both the cytoplasm and nucleus of neoplastic cells (Immunofluorescence, 20 × magnification); G: HIF-1α expression was significantly different between the TI and ITF regions (aP = 0.0134). Additionally, a significant difference was observed between TI and NOM (bP = 0.0115).
- Citation: Silveira FM, Schuch LF, Pereira-Prado V, Molina-Frechero N, Lopez-Verdin S, Gómez Palacio-Gastélum M, Arocena M, Niklander S, Sicco E, Bologna-Molina R. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α at the invasive tumor front in oral squamous cell carcinoma. World J Exp Med 2025; 15(2): 102175
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315x/full/v15/i2/102175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v15.i2.102175