Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Exp Med. Mar 20, 2024; 14(1): 86898
Published online Mar 20, 2024. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v14.i1.86898
Published online Mar 20, 2024. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v14.i1.86898
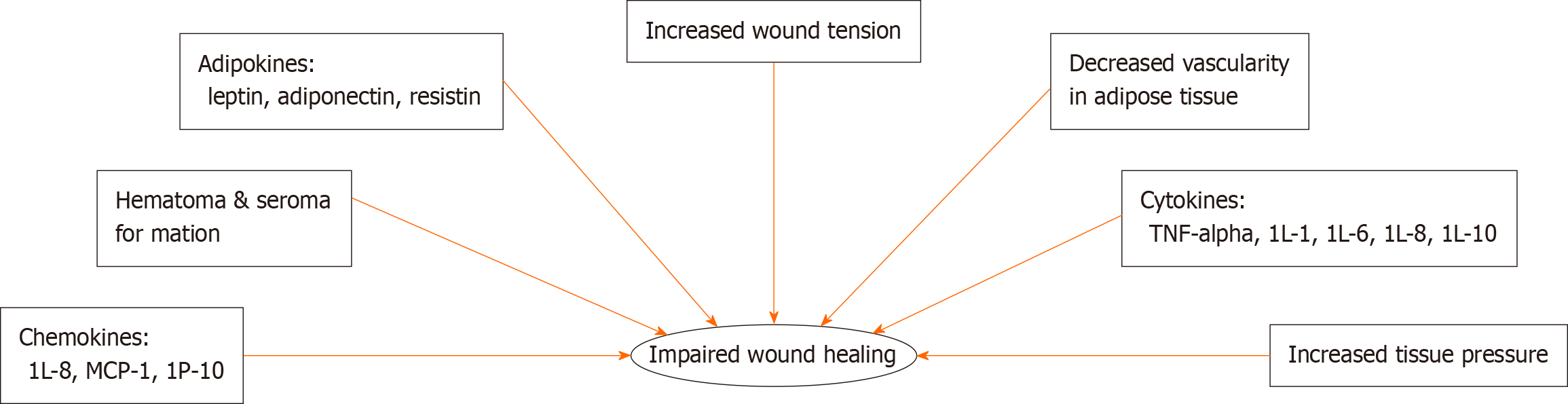
Figure 2 Factors related to wound healing impairment in obesity.
Obesity is characterized by a chronic inflammatory state that is associated with changes mediated by varying levels of adipokines, chemokines, and cytokines. In addition to these chemical signals, physiologic changes including increased tissue pressure and decreased vascularity of adipose tissue also contribute to poor wound healing outcomes. MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; IP-10: Interferon-gamma-inducible protein 10; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Cotterell A, Griffin M, Downer MA, Parker JB, Wan D, Longaker MT. Understanding wound healing in obesity. World J Exp Med 2024; 14(1): 86898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315x/full/v14/i1/86898.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v14.i1.86898