Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Exp Med. May 20, 2017; 7(2): 49-57
Published online May 20, 2017. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v7.i2.49
Published online May 20, 2017. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v7.i2.49
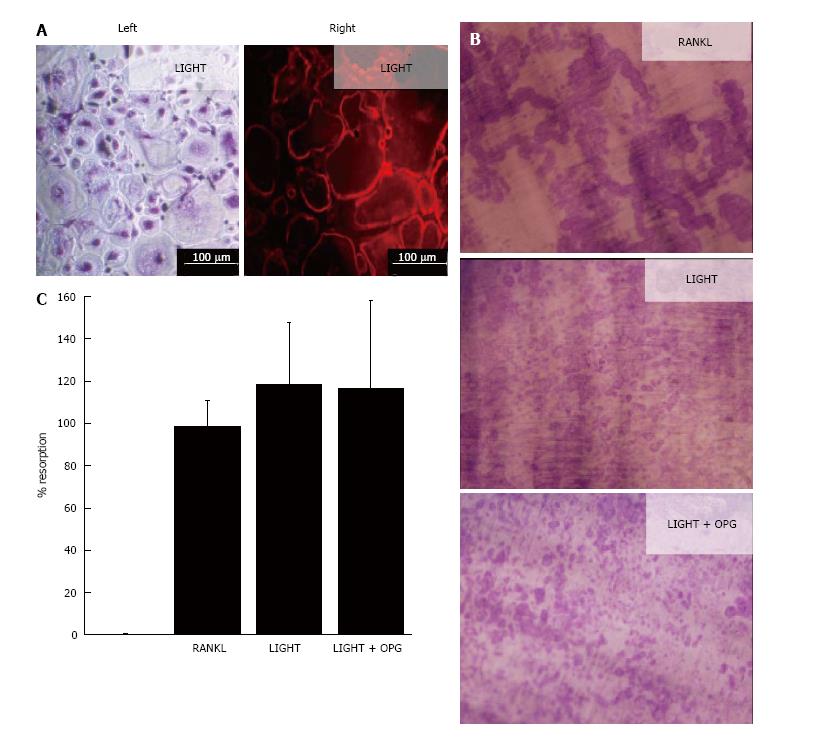
Figure 1 LIGHT induces receptor-activator nuclear factor kappa-B ligand-independent osteoclastogenesis from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid macrophages.
A: Osteoclast differentiation in 14-d cultures of RA SF macrophages incubated with M-CSF and LIGHT showing (left) TRAP+ multinucleated osteoclasts and (right) F actin-ring formation; B: Dentine slices stained with Toluidine blue showing lacunar resorption in 14-d RA SF macrophage cultures treated with M-CSF and sRANKL, LIGHT or LIGHT ± OPG; C: Percentage surface area lacunar resorption on dentine slices in LIGHT- (± OPG) treated SF macrophage cultures relative to sRANKL - treated controls; data is expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments where each condition was carried out in triplicate. RANKL: Receptor-activator nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; SF: Synovial fluid; M-CSF: Macrophage-colony stimulating factor; OPG: Osteoprotegerin.
- Citation: Sabokbar A, Afrough S, Mahoney DJ, Uchihara Y, Swales C, Athanasou NA. Role of LIGHT in the pathogenesis of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. World J Exp Med 2017; 7(2): 49-57
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v7/i2/49.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v7.i2.49