Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Exp Med. Nov 20, 2015; 5(4): 225-231
Published online Nov 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i4.225
Published online Nov 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i4.225
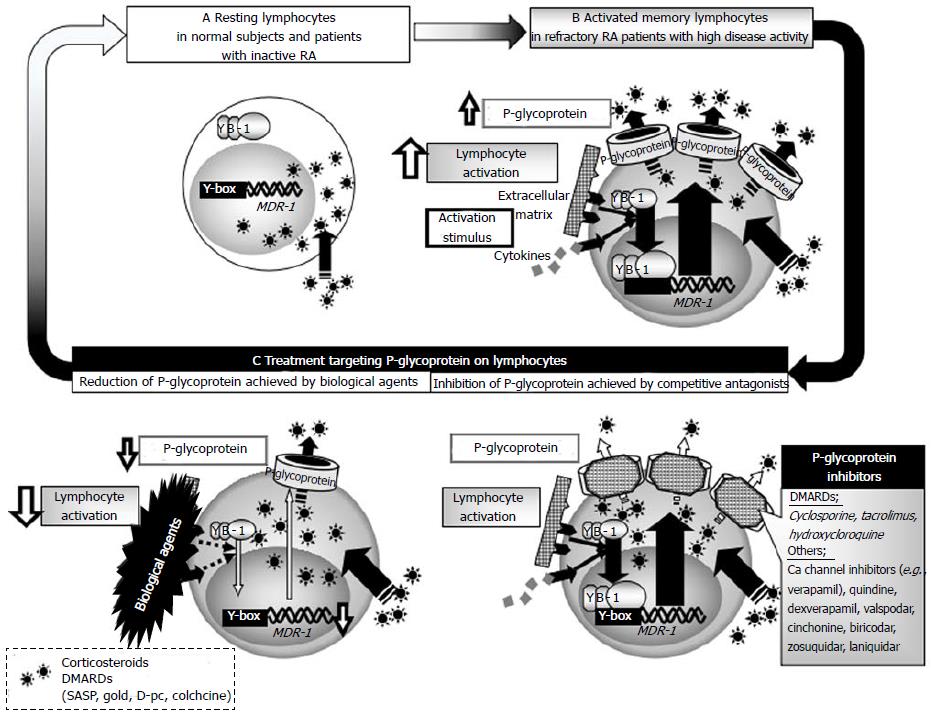
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the relevance of P-glycoprotein to drug resistance in rheumatoid arthritis.
A: Y-box-binding protein-1 is located in the cytoplasm of lymphocytes and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is only marginally expressed on normal lymphocytes of normal subjects and patients with inactive RA; B: In patients with highly active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), various stimuli induce P-gp expression on lymphocytes, which leads to active efflux of drugs from lymphocytes, resulting in drug-unresponsiveness and failure to control disease activity; C: Reduction of P-gp achieved by intensive immunosuppressive therapy and inhibition of P-gp by competitive antagonists, such as cyclosporine, could overcome P-gp-related drug-resistance in patients with highly active RA. DMARDs: Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs; MDR-1: Multidrug resistance 1.
- Citation: Tsujimura S, Tanaka Y. Disease control by regulation of P-glycoprotein on lymphocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. World J Exp Med 2015; 5(4): 225-231
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v5/i4/225.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v5.i4.225