Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Exp Med. Nov 20, 2015; 5(4): 218-224
Published online Nov 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i4.218
Published online Nov 20, 2015. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i4.218
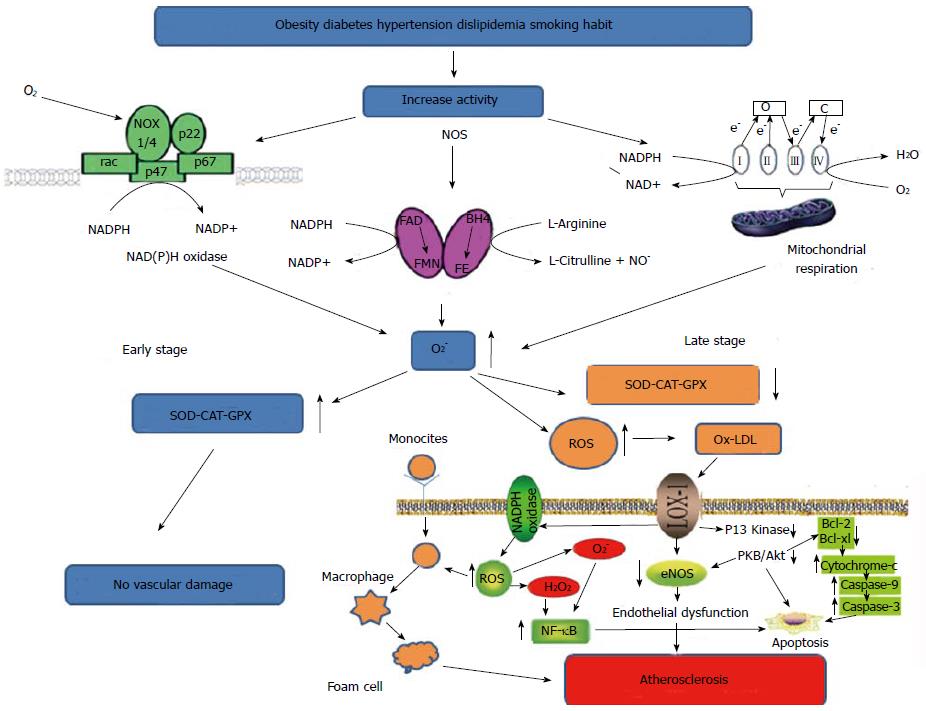
Figure 1 Biochemical events that favor the increase of reactive oxygen species.
In the early stages of CAD, ROS do not cause damage due to the presence of an enzymatic compensatory mechanism. In late stage this mechanism is saturated and no longer allows an efficient defense, so that other biochemical events lead to vascular damage. ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; CAT: Catalase; GPX: Glutathione peroxidase; CAD: Coronary artery disease; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase; LOX-1: Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; FAD: Flavin adenine dinucelotide; BH4: Tetrahydrobiopterin; FE: Heme iron; FMN: Flavin mononucleotide.
- Citation: Lubrano V, Balzan S. Enzymatic antioxidant system in vascular inflammation and coronary artery disease. World J Exp Med 2015; 5(4): 218-224
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v5/i4/218.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v5.i4.218